Progress towards a clinically-successful ATR inhibitor for cancer therapy
- PMID: 34909652
- PMCID: PMC8663972
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100017
Progress towards a clinically-successful ATR inhibitor for cancer therapy
Abstract
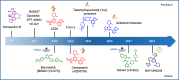
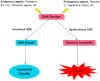
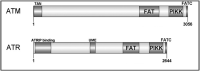
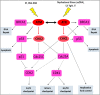
The DNA damage response (DDR) is now known to play an important role in both cancer development and its treatment. Targeting proteins such as ATR (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated and Rad3-related) kinase, a major regulator of DDR, has demonstrated significant therapeutic potential in cancer treatment, with ATR inhibitors having shown anti-tumour activity not just as monotherapies, but also in potentiating the effects of conventional chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy. This review focuses on the biology of ATR, its functional role in cancer development and treatment, and the rationale behind inhibition of this target as a therapeutic approach, including evaluation of the progress and current status of development of potent and specific ATR inhibitors that have emerged in recent decades. The current applications of these inhibitors both in preclinical and clinical studies either as single agents or in combinations with chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy are also extensively discussed. This review concludes with some insights into the various concerns raised or observed with ATR inhibition in both the preclinical and clinical settings, with some suggested solutions.
Keywords: ATM; ATR; ATR inhibitors; Chemo- and radiosensitisers; DDR.
Crown Copyright © 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
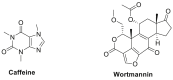
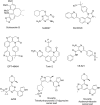
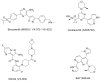
References
-
- Abraham R.T. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2177–2196. - PubMed
-
- Alderton G.K., et al. Seckel syndrome exhibits cellular features demonstrating defects in the ATR-signalling pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004;13:3127–3138. - PubMed
-
- Arris C.E., et al. Identification of novel purine and pyrimidine cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors with distinct molecular interactions and tumor cell growth inhibition profiles. J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:2797–2804. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

