This is a preprint.
COVID-19 infections post-vaccination by HIV status in the United States
- PMID: 34909791
- PMCID: PMC8669858
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.12.02.21267182
COVID-19 infections post-vaccination by HIV status in the United States
Update in
-
Analysis of Postvaccination Breakthrough COVID-19 Infections Among Adults With HIV in the United States.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Jun 1;5(6):e2215934. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.15934. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35671054 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Importance: Recommendations for additional doses of COVID vaccine are restricted to people with HIV who have advanced disease or unsuppressed HIV viral load. Understanding SARS-CoV-2 infection risk post-vaccination among PWH is essential for informing vaccination guidelines.
Objective: Estimate the risk of breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated people with (PWH) and without (PWoH) HIV in the US.
Design setting and participants: The Corona-Infectious-Virus Epidemiology Team (CIVET)-II cohort collaboration consists of 4 longitudinal cohorts from integrated health systems and academic health centers. Each cohort identified individuals ≥18 years old, in-care, and fully vaccinated for COVID-19 through 30 June 2021. PWH were matched to PWoH on date fully vaccinated, age group, race/ethnicity, and sex at birth. Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years and cumulative incidence of breakthrough infections with 95% confidence intervals ([,]) were estimated by HIV status. Cox proportional hazards models estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) of breakthrough infections by HIV status adjusting for demographic factors, prior COVID-19 illness, vaccine type (BNT162b2, [Pfizer], mRNA-1273 [Moderna], Jansen Ad26.COV2.S [J&J]), calendar time, and cohort. Risk factors for breakthroughs among PWH, were also investigated.
Exposure: HIV infection.
Outcome: COVID-19 breakthrough infections, defined as laboratory evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 diagnosis after an individual was fully vaccinated.
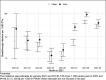
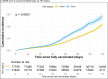
Results: Among 109,599 individuals (31,840 PWH and 77,759 PWoH), the rate of breakthrough infections was higher in PWH versus PWoH: 44 [41, 48] vs. 31 [29, 33] per 1,000 person-years. Cumulative incidence at 210 days after date fully vaccinated was low, albeit higher in PWH versus PWoH overall (2.8% versus 2.1%, log-rank p<0.001, risk difference=0.7% [0.4%, 1.0%]) and within each vaccine type. Breakthrough infection risk was 41% higher in PWH versus PWoH (aHR=1.41 [1.28, 1.56]). Among PWH, younger age (18-24 versus 45-54), history of COVID-19 prior to fully vaccinated date, and J&J vaccination (versus Pfizer) were associated with increased risk of breakthroughs. There was no association of breakthrough with HIV viral load suppression or CD4 count among PWH.
Conclusions and relevance: COVID-19 vaccination is effective against infection with SARS-CoV-2 strains circulating through 30 Sept 2021. PWH have an increased risk of breakthrough infections compared to PWoH. Recommendations for additional vaccine doses should be expanded to all PWH.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01 DA011602/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 EY013707/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010176/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM133807/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020790/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI131895/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA037788/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CP001004/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036297/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI124794/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007583/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA000432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008057/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008052/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI110527/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R34 DA045592/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI093197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI118591/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI065298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA013566/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP055504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000083/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146240/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008067/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA020794/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
