Coronary blood vessels from distinct origins converge to equivalent states during mouse and human development
- PMID: 34910626
- PMCID: PMC8673841
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.70246
Coronary blood vessels from distinct origins converge to equivalent states during mouse and human development
Abstract
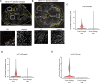
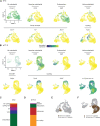
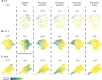
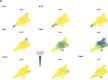
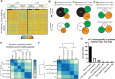
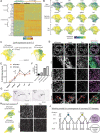
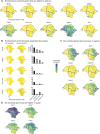
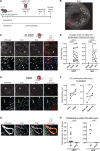
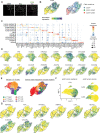
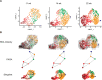
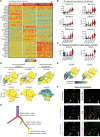
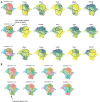
Most cell fate trajectories during development follow a diverging, tree-like branching pattern, but the opposite can occur when distinct progenitors contribute to the same cell type. During this convergent differentiation, it is unknown if cells 'remember' their origins transcriptionally or whether this influences cell behavior. Most coronary blood vessels of the heart develop from two different progenitor sources-the endocardium (Endo) and sinus venosus (SV)-but whether transcriptional or functional differences related to origin are retained is unknown. We addressed this by combining lineage tracing with single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) in embryonic and adult mouse hearts. Shortly after coronary development begins, capillary endothelial cells (ECs) transcriptionally segregated into two states that retained progenitor-specific gene expression. Later in development, when the coronary vasculature is well established but still remodeling, capillary ECs again segregated into two populations, but transcriptional differences were primarily related to tissue localization rather than lineage. Specifically, ECs in the heart septum expressed genes indicative of increased local hypoxia and decreased blood flow. Adult capillary ECs were more homogeneous with respect to both lineage and location. In agreement, SV- and Endo-derived ECs in adult hearts displayed similar responses to injury. Finally, scRNAseq of developing human coronary vessels indicated that the human heart followed similar principles. Thus, over the course of development, transcriptional heterogeneity in coronary ECs is first influenced by lineage, then by location, until heterogeneity declines in the homeostatic adult heart. These results highlight the plasticity of ECs during development, and the validity of the mouse as a model for human coronary development.
Keywords: convergent differentiation; developmental biology; heart development; human; human mouse comparison; mouse; vascular development.
© 2021, Phansalkar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RP, JK, MZ, SK, RJ, SQ, IW, DB, VW, GD, KR No competing interests declared
Figures







References
-
- Aibar S, González-Blas CB, Moerman T, Huynh-Thu VA, Imrichova H, Hulselmans G, Rambow F, Marine JC, Geurts P, Aerts J, van den Oord J, Atak ZK, Wouters J, Aerts S. SCENIC: single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering. Nature Methods. 2017;14:1083–1086. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arita Y, Nakaoka Y, Matsunaga T, Kidoya H, Yamamizu K, Arima Y, Kataoka-Hashimoto T, Ikeoka K, Yasui T, Masaki T, Yamamoto K, Higuchi K, Park JS, Shirai M, Nishiyama K, Yamagishi H, Otsu K, Kurihara H, Minami T, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Koh GY, Mochizuki N, Takakura N, Sakata Y, Yamashita JK, Komuro I. Myocardium-derived angiopoietin-1 is essential for coronary vein formation in the developing heart. Nature Communications. 2014;5:4552. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5552. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asp M, Giacomello S, Larsson L, Wu C, Fürth D, Qian X, Wärdell E, Custodio J, Reimegård J, Salmén F, Österholm C, Ståhl PL, Sundström E, Åkesson E, Bergmann O, Bienko M, Månsson-Broberg A, Nilsson M, Sylvén C, Lundeberg J. A spatiotemporal organ-wide gene expression and cell atlas of the developing human heart. Cell. 2019;179:1647–1660. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.025. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

