High SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and Low CCL5 Expression Levels in the Upper Respiratory Tract Are Associated With COVID-19 Severity
- PMID: 34910814
- PMCID: PMC8754799
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab604
High SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and Low CCL5 Expression Levels in the Upper Respiratory Tract Are Associated With COVID-19 Severity
Abstract
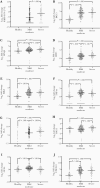
Mucosal immune response in the upper respiratory tract is crucial for initial control of viral replication, clearance of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and progression of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We analyzed SARS-CoV-2 RNA load and expression of selected immune genes in the upper respiratory tract (nasopharynx) of 255 SARS-CoV-2-infected patients and evaluated their association with severe COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 replication in nasopharyngeal mucosa induces expression of several innate immune genes. High SARS-CoV-2 viral load and low CCL5 expression levels were associated with intensive care unit admission or death, although CCL5 was the best predictor of COVID-19 severity.
Keywords: CCL5; COVID-19; ICU; SARS-CoV-2; death; gene expression; innate immunity; nasopharynx; viral load.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reply to Pati et al.J Infect Dis. 2022 May 16;225(10):1866-1868. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac027. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35091740 No abstract available.
-
CCL5 rs2107538 Variant Is Associated With Protection Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Related Mortality: A Population-Based Study.J Infect Dis. 2022 May 16;225(10):1865-1866. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac026. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35091748 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

