Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 in Adults in the United States and Mexico
- PMID: 34910859
- PMCID: PMC8693692
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116185
Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 in Adults in the United States and Mexico
Abstract
Background: NVX-CoV2373 is an adjuvanted, recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine that was shown to have clinical efficacy for the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) in phase 2b-3 trials in the United Kingdom and South Africa, but its efficacy had not yet been tested in North America.
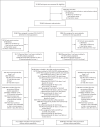
Methods: We conducted a phase 3, randomized, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled trial in the United States and Mexico during the first half of 2021 to evaluate the efficacy and safety of NVX-CoV2373 in adults (≥18 years of age) who had not had severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Participants were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive two doses of NVX-CoV2373 or placebo 21 days apart. The primary objective was to determine vaccine efficacy against reverse-transcriptase-polymerase-chain-reaction-confirmed Covid-19 occurring at least 7 days after the second dose. Vaccine efficacy against moderate-to-severe disease and against different variants was also assessed.
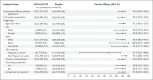
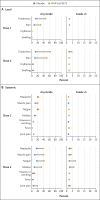
Results: Of the 29,949 participants who underwent randomization between December 27, 2020, and February 18, 2021, a total of 29,582 (median age, 47 years; 12.6% ≥65 years of age) received at least one dose: 19,714 received vaccine and 9868 placebo. Over a period of 3 months, 77 cases of Covid-19 were noted - 14 among vaccine recipients and 63 among placebo recipients (vaccine efficacy, 90.4%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 82.9 to 94.6; P<0.001). Ten moderate and 4 severe cases occurred, all in placebo recipients, yielding vaccine efficacy against moderate-to-severe disease of 100% (95% CI, 87.0 to 100). Most sequenced viral genomes (48 of 61, 79%) were variants of concern or interest - largely B.1.1.7 (alpha) (31 of the 35 genomes for variants of concern, 89%). Vaccine efficacy against any variant of concern or interest was 92.6% (95% CI, 83.6 to 96.7). Reactogenicity was mostly mild to moderate and transient but was more frequent among NVX-CoV2373 recipients than among placebo recipients and was more frequent after the second dose than after the first dose.
Conclusions: NVX-CoV2373 was safe and effective for the prevention of Covid-19. Most breakthrough cases were caused by contemporary variant strains. (Funded by Novavax and others; PREVENT-19 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04611802.).
Copyright © 2021 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
In adults who had not had COVID-19, Novavax vaccine had 90% efficacy at ≥7 d after the second dose.Ann Intern Med. 2022 May;175(5):JC52. doi: 10.7326/J22-0028. Epub 2022 May 3. Ann Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35500261
References
-
- Slaoui M, Hepburn M. Developing safe and effective Covid vaccines — Operation Warp Speed’s strategy and approach. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1701-1703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI148689/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI148575/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000207/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- S10 AI174104/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068614/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068618/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI148684/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
