Serotonergic Regulation of Hepatic Energy Metabolism
- PMID: 34911172
- PMCID: PMC8743581
- DOI: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1331
Serotonergic Regulation of Hepatic Energy Metabolism
Abstract
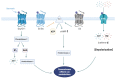
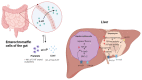
The liver is a vital organ that regulates systemic energy metabolism and many physiological functions. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the commonest cause of chronic liver disease and end-stage liver failure. NAFLD is primarily caused by metabolic disruption of lipid and glucose homeostasis. Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT]) is a biogenic amine with several functions in both the central and peripheral systems. 5-HT functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain and a hormone in peripheral tissues to regulate systemic energy homeostasis. Several recent studies have proposed various roles of 5-HT in hepatic metabolism and inflammation using tissue-specific knockout mice and 5-HT-receptor agonists/antagonists. This review compiles the most recent research on the relationship between 5-HT and hepatic metabolism, and the role of 5-HT signaling as a potential therapeutic target in NAFLD.
Keywords: Liver; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Serotonin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gut Barrier Proteins Mediate Liver Regulation by the Effects of Serotonin on the Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(10):978-984. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666200615171928. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 32538722 Review.
-
Disturbed Vitamin A Metabolism in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).Nutrients. 2017 Dec 29;10(1):29. doi: 10.3390/nu10010029. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29286303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the liver-gut peripheral neural axis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathologies via hepatic HTR2A.Dis Model Mech. 2022 Jul 1;15(7):dmm049612. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049612. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Dis Model Mech. 2022. PMID: 35765850 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Role of the Central and Peripheral Serotonin Network on Feeding Signals in Metabolic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 29;23(3):1600. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031600. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrg4 promotes fuel oxidation and a healthy adipokine profile to ameliorate diet-induced metabolic disorders.Mol Metab. 2017 Jun 21;6(8):863-872. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.03.016. eCollection 2017 Aug. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28752050 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of gut microbes in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.Tzu Chi Med J. 2023 Jul 11;35(4):279-289. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_86_23. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. Tzu Chi Med J. 2023. PMID: 38035063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of mitogens in normal and pathological liver regeneration.Hepatol Commun. 2025 Apr 30;9(5):e0692. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000692. eCollection 2025 May 1. Hepatol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40304568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of BMP6 on Serotonin and Glucose Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7842. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147842. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063084 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin in the regulation of systemic energy metabolism.J Diabetes Investig. 2022 Oct;13(10):1639-1645. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13879. Epub 2022 Jul 23. J Diabetes Investig. 2022. PMID: 35762288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal nutrient metabolism in the liver during pregnancy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 20;15:1295677. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1295677. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38572473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abai B. StatPearls. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Chapter, Physiology, liver. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535438 .
-
- Byrne CD, Targher G. NAFLD: a multisystem disease. J Hepatol. 2015;62(1 Suppl):S47–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

