Artificial intelligence-aided clinical annotation of a large multi-cancer genomic dataset
- PMID: 34911934
- PMCID: PMC8674229
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27358-6
Artificial intelligence-aided clinical annotation of a large multi-cancer genomic dataset
Abstract
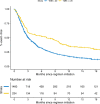
To accelerate cancer research that correlates biomarkers with clinical endpoints, methods are needed to ascertain outcomes from electronic health records at scale. Here, we train deep natural language processing (NLP) models to extract outcomes for participants with any of 7 solid tumors in a precision oncology study. Outcomes are extracted from 305,151 imaging reports for 13,130 patients and 233,517 oncologist notes for 13,511 patients, including patients with 6 additional cancer types. NLP models recapitulate outcome annotation from these documents, including the presence of cancer, progression/worsening, response/improvement, and metastases, with excellent discrimination (AUROC > 0.90). Models generalize to cancers excluded from training and yield outcomes correlated with survival. Among patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors, we confirm that high tumor mutation burden is associated with superior progression-free survival ascertained using NLP. Here, we show that deep NLP can accelerate annotation of molecular cancer datasets with clinically meaningful endpoints to facilitate discovery.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Kehl reports serving as a consultant/advisor to Aetion, receiving funding from the American Association for Cancer Research related to this work, and receiving honoraria from Roche and IBM. Dr. Schrag reports compensation from JAMA for serving as an Associate Editor and from Pfizer for giving a talk at a symposium. She has received research funding from the American Association for Cancer Research related to this work and research funding from GRAIL for serving as the site-PI of a clinical trial. Unrelated to this work, Dr. Choueiri reports serving on research/advisory boards and receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca, Aravive, Aveo, Bayer, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Eisai, EMD Serono, Exelixis, GlaxoSmithKline, IQVA, Ipsen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi/Aventis, Takeda, Tempest, Up-To-Date, CME events (Peerview, OncLive and others). Dr. Van Allen reports serving in advisory/consulting roles to Tango Therpeutics, Genome Medical, Invitae, Enara Bio, Janssen, Manifold Bio, and Monte Rosa; receiving research support from Novartis and BMS; holding equity in Tango Therapeutics, Genome Medical, Syapse, Enara Bio, Manifold Bio, Microsoft, and Monte Rosa; and receiving travel reimbursement from Roche/Genentech. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- AACR Project GENIE Consortium. AACR Project GENIE: Powering Precision Medicine through an International Consortium. Cancer Disco. 2017;7:818–831. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0151. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

