Essential Oil Nanoemulsion as Eco-Friendly and Safe Preservative: Bioefficacy Against Microbial Food Deterioration and Toxin Secretion, Mode of Action, and Future Opportunities
- PMID: 34912311
- PMCID: PMC8667777
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.751062
Essential Oil Nanoemulsion as Eco-Friendly and Safe Preservative: Bioefficacy Against Microbial Food Deterioration and Toxin Secretion, Mode of Action, and Future Opportunities
Abstract
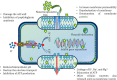
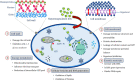
Microbes are the biggest shareholder for the quantitative and qualitative deterioration of food commodities at different stages of production, transportation, and storage, along with the secretion of toxic secondary metabolites. Indiscriminate application of synthetic preservatives may develop resistance in microbial strains and associated complications in human health with broad-spectrum environmental non-sustainability. The application of essential oils (EOs) as a natural antimicrobial and their efficacy for the preservation of foods has been of present interest and growing consumer demand in the current generation. However, the loss in bioactivity of EOs from fluctuating environmental conditions is a major limitation during their practical application, which could be overcome by encapsulating them in a suitable biodegradable and biocompatible polymer matrix with enhancement to their efficacy and stability. Among different nanoencapsulated systems, nanoemulsions effectively contribute to the practical applications of EOs by expanding their dispersibility and foster their controlled delivery in food systems. In line with the above background, this review aims to present the practical application of nanoemulsions (a) by addressing their direct and indirect (EO nanoemulsion coating leading to active packaging) consistent support in a real food system, (b) biochemical actions related to antimicrobial mechanisms, (c) effectiveness of nanoemulsion as bio-nanosensor with large scale practical applicability, (d) critical evaluation of toxicity, safety, and regulatory issues, and (e) market demand of nanoemulsion in pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals along with the current challenges and future opportunities.
Keywords: biodeterioration; eco-friendly; essential oil; food preservative; nanoemulsion; toxins.
Copyright © 2021 Maurya, Singh, Das, Prasad, Kedia, Upadhyay, Dubey and Dwivedy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abd-Elsalam K. A., Khokhlov A. R. (2015). Eugenol oil nanoemulsion: antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum and phytotoxicity on cottonseeds. Appl. Nanosci. 5 255–265. 10.1007/s13204-014-0398-y - DOI
-
- Agarwal Y., Rajinikanth P. S., Ranjan S., Tiwari U., Balasubramnaiam J., Pandey P., et al. (2021). Curcumin loaded polycaprolactone-/polyvinyl alcohol-silk fibroin based electrospun nanofibrous mat for rapid healing of diabetic wound: an in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 176 376–386. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.025 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aldars-Garcia L., Ramos A. J., Sanchis V., Marin S. (2016). Modeling postharvest mycotoxins in foods: recent research. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 11 46–50. 10.1016/j.cofs.2016.09.005 - DOI
-
- Alizadeh A. M., Hashempour-Baltork F., Khaneghah A. M., Hosseini H. (2020). New perspective approaches in controlling fungi and mycotoxins in food using emerging and green technologies. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 39 7–15. 10.1016/j.cofs.2020.12.006 - DOI
-
- Almasi L., Radi M., Amiri S., McClements D. J. (2021). Fabrication and characterization of antimicrobial biopolymer films containing essential oil-loaded microemulsions or nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 117:106733. 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106733 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources