The Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 34912342
- PMCID: PMC8666442
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.773171
The Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
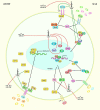
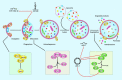
Osteoarthritis (OS) is the most frequent degenerative condition in the joints, disabling many adults. Several abnormalities in the articular cartilage, subchondral bone, synovial tissue, and meniscus have been detected in the course of OA. Destruction of articular cartilage, the formation of osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, and hyperplasia of synovial tissue are hallmarks of OA. More recently, several investigations have underscored the regulatory roles of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in OA development. Different classes of non-coding RNAs, including long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), have been reported to affect the development of OA. The expression level of these transcripts has also been used as diagnostic tools in OA. In the present article, we aimed at reporting the role of these transcripts in this process. We need to give a specific angle on the pathology to provide meaningful thoughts on it.
Keywords: circRNA; expression; lncRNA; miRNA; ncRNAs; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2021 Ghafouri-Fard, Poulet, Malaise, Abak, Mahmud Hussen, Taheriazam, Taheri and Hallajnejad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- van Lent PL, Blom AB, Schelbergen RF, Slöetjes A, Lafeber FP, Lems WF, et al. Active Involvement of Alarmins S100A8 and S100A9 in the Regulation of Synovial Activation and Joint Destruction During Mouse and Human Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum (2012) 64(5):1466–76. doi: 10.1002/art.34315 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

