Systematic Review of Tongxinluo Capsule on the Therapeutic Effect and Hemorheology of Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack
- PMID: 34912462
- PMCID: PMC8668333
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5541768
Systematic Review of Tongxinluo Capsule on the Therapeutic Effect and Hemorheology of Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of Tongxinluo capsule in the treatment of transient ischemic attack (TIA) and its effect on hemorheology, thereby providing scientific basis for clinical decision making.
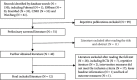
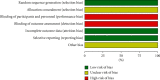
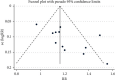
Methods: A comprehensive and systematic literature retrieval was conducted in the CNKI, Wanfang database, SinoMed, EMbase, and PubMed to screen the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of Tongxinluo capsule in the treatment of TIA. The retrieval time was from the inception of each database to September 10, 2020. Endnote X9 was used to screen the literature. Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing risk of bias was used to evaluate the quality of the included studies. Stata16.0 statistical software was used for meta-analysis.
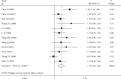
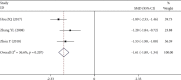
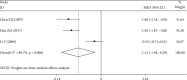
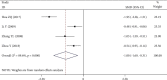
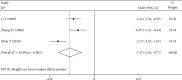
Results: A total of 12 RCTs were included, involving 946 subjects. (1) The clinical efficacy of the Tongxinluo group was better than that of the control group (RR = 1.19, 95% CI (1.09, 1.30), P ≤ 0.001). (2) The hemorheological characteristics of the Tongxinluo group were significantly improved compared with those of the control group (whole blood high shear viscosity: SMD = -1.61, 95% CI (-1.89, -1.34); P ≤ 0.001, whole blood low shear viscosity: SMD = -1.06, 95% CI (-1.31, -0.80), P ≤ 0.001, fibrinogen: SMD = -1.12, 95% CI (-1.94, -0.29), P = 0.008, plasma specific viscosity: SMD = -1.00, 95% CI (-1.69, -0.31), P = 0.004, and hematocrit: SMD = -1.47, 95% CI (-2.16, -0.77), P ≤ 0.001). (3) There was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the Tongxinluo group and control group (RR = 7.76, 95% CI (0.98, 61.28), P = 0.052).
Conclusion: Tongxinluo capsule is superior to conventional treatment in improving clinical overall response rate and hemorheological indexes and is relatively safe. Due to the deficiencies of the existing studies, more high-quality studies with rigorous design are required for further verification.
Copyright © 2021 Peng Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Gao C., Li W., Lin B., Zhan T. T., Lin Z. C. Predictive ability of ABCD∼2 score for mid-term cerebral infarction and death after transient cerebral ischemia. Chinese Journal of Neurology . 2011;10(9):896–899.
-
- Yin S. H. Analysis of the efficacy and safety of aspirin combined with clopidogrel in the treatment of intractable transient ischemic attack. Electronic Journal of Clinical Medical Literature . 2017;4(68):13293–13294.
-
- Yang F. X., Wang N. Research progress of hemorheology in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Journal of Anhui Vocational and Technical College of Health . 2015;14(04):44–47.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

