COVID-19 and the differences in physiological background between children and adults and their clinical consequences
- PMID: 34913353
- PMCID: PMC8884370
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.934759
COVID-19 and the differences in physiological background between children and adults and their clinical consequences
Abstract
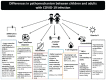
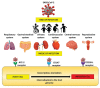
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has indeed been one of the most significant problems facing the world in the last decade. It has affected (directly or indirectly) the entire population and all age groups. Children have accounted for 1.7 % to 2 % of the diagnosed cases of COVID-19. COVID-19 in children is usually associated with a mild course of the disease and a better survival rate than in adults. In this review, we investigate the different mechanisms which underlie this observation. Generally, we can say that the innate immune response of children is strong because they have a trained immunity, allowing the early control of infection at the site of entry. Suppressed adaptive immunity and a dysfunctional innate immune response is seen in adult patients with severe infections but not in children. This may relate to immunosenescence in the elderly. Another proposed factor is the different receptors for SARS-CoV-2 and their differences in expression between these age groups. In infants and toddlers, effective immune response to viral particles can be modulated by the pre-existing non-specific effect of live attenuated vaccines on innate immunity and vitamin D prophylaxis. However, all the proposed mechanisms require verification in larger cohorts of patients. Our knowledge about SARS-CoV-2 is still developing.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- AGUAIR JA, TREMBLAY BJ, MANSFIELD MJ, WOODY O, LOBB B, BANERJEE A, CHANDIRAMONAH A, TIESSEN N, CAO Q, DVORKIN-GHEVA A, REVILL S, MILLER MS, CARLSTEN C, ORGAN L, JOSEPH C, JOHN A, HANSON P, AUSTIN RC, McMANUS BM, JENKINS G, ET AL. Gene expression and in situ protein profiling of candidate SARS-CoV-2 receptors in human airway epithelial cells and lung tissue. Eur Respir J. 2020;56:2001123. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01123-2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- BASTARD P, ROSEN LB, ZHANG Q, HOFFMANN HH, CHBIHI M, Le VOYER T, ROSAIN J, PHILIPPOT Q, SEELEUTHER Y, GERVAIS A, MATERNA M, De OLIVIERA PMN, MAIA MLS, DINIS ANO BOM AP, AZAMOR T, ARAUJO DA, CONCEICAO D, GOUDORIS E, HOMMA A, SLESAK G, SCHAFER J, ET AL. Auto-antibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. J Exp Med. 218:e20202486. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202486. - DOI
-
- BOBCAKOVA A, PETRISKOVA J, VYSEHRADSKY R, KOCAN I, KAPUSTOVA L, BARNOVA M, DIAMANT Z, JESENAK M. Immune profile in patients with COVID-19: Lymphocytes exhaustion markers in relationship to clinical outcome. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:646688. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.646688. - DOI - PMC - PubMed