Validation of the Dutch translation of the Paris Arousal Disorders Severity Scale for non-REM parasomnias in a 1-year and 1-month version
- PMID: 34913868
- PMCID: PMC8974369
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.9830
Validation of the Dutch translation of the Paris Arousal Disorders Severity Scale for non-REM parasomnias in a 1-year and 1-month version
Abstract
Study objectives: We created a Dutch version of the Paris Arousal Disorders Severity Scale (PADSS), which assesses non-rapid eye movement (NREM) parasomnia symptoms over the past year (PADSS-year). This questionnaire was previously validated in patients with sleep walking and/or sleep terrors (SW/ST). We validated the questionnaire in SW/ST patients, and in a broader population, including patients with confusional arousals, comorbidities, and medication users ("other NREM parasomnias"). Furthermore, we introduced a version covering the past month (PADSS-month), with the potential purpose of evaluating symptom evolution and treatment response.
Methods: We compared PADSS scores among 54 SW/ST patients, 34 age-matched controls, and 23 patients with other NREM parasomnias. We evaluated discriminative capacity, internal consistency, and construct validity. Furthermore, we assessed the test-retest reliability and treatment response of PADSS-month.
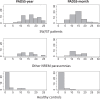
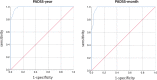
Results: Healthy controls scored significantly lower than both patient groups. We found an excellent diagnostic accuracy (area under the curve PADSS-year 0.990, PADSS-month 0.987) and an acceptable internal consistency. Exploratory factor analysis identified 3 components: "behaviors outside the bed," "behaviors in/around the bed," and "violent behaviors," with the former 2 factors reflecting the distinction between SW and ST. PADSS-month showed an acceptable test-retest reliability (0.75). Additionally, PADSS-month significantly decreased after pharmaceutical and/or behavioral treatment. This change was correlated with the clinical impression of the caregiver, implying that PADSS-month is sensitive to treatment effects.
Conclusions: The Dutch PADSS questionnaire can be used as a screening tool in a broad population of patients with NREM parasomnia, not only SW/ST. Furthermore, we validated a PADSS-month version to assess the evolution of symptoms and treatment effect.
Citation: van Mierlo P, Hermans L, Arnulf I, Pijpers A, Overeem S, van Gilst M. Validation of the Dutch translation of the Paris Arousal Disorders Severity Scale for non-REM parasomnias in a 1-year and 1-month version. J Clin Sleep Med. 2022;18(4):1135-1143.
Keywords: NREM parasomnia; sleep terror; sleepwalking.
© 2022 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have seen and approved the manuscript. S. Overeem consulted for Bioprojet, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, UCB Pharma, and Takeda, all paid to the institution, and not related to the present work. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Castelnovo A , Lopez R , Proserpio P , Nobili L , Dauvilliers Y . NREM sleep parasomnias as disorders of sleep-state dissociation . Nat Rev Neurol. 2018. ; 14 ( 8 ): 470 – 481 . - PubMed
-
- Zadra A , Desautels A , Petit D , Montplaisir J . Somnambulism: clinical aspects and pathophysiological hypotheses . Lancet Neurol. 2013. ; 12 ( 3 ): 285 – 294 . - PubMed
-
- Lundetræ RS , Saxvig IW , Pallesen S , Aurlien H , Lehmann S , Bjorvatn B . Prevalence of parasomnias in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. A registry-based cross-sectional study . Front Psychol. 2018. ; 9 : 1140 https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01140 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

