Automation improves repeatability of retinal oximetry measurements
- PMID: 34914738
- PMCID: PMC8675673
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260120
Automation improves repeatability of retinal oximetry measurements
Abstract
Purpose: Retinal oximetry is a technique based on spectrophotometry where images are analyzed with software capable of calculating vessel oxygen saturation and vessel diameter. In this study, the effect of automation of measurements of retinal vessel oxygen saturation and vessel diameter is explored.
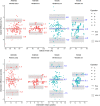
Methods: Until now, operators have had to choose each vessel segment to be measured explicitly. A new, automatic version of the software automatically selects the vessels once the operator defines a measurement area. Five operators analyzed image pairs from the right eye of 23 healthy subjects with semiautomated retinal oximetry analysis software, Oxymap Analyzer (v2.5.1), and an automated version (v3.0). Inter- and intra-operator variability was investigated using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) between oxygen saturation measurements of vessel segments in the same area of the retina.
Results: For semiautomated saturation measurements, the inter-rater ICC was 0.80 for arterioles and venules. For automated saturation measurements, the inter-rater ICC was 0.97 for arterioles and 0.96 for venules. For semiautomated diameter measurements, the inter-rater ICC was 0.71 for arterioles and venules. For automated diameter measurements the inter-rater ICC was 0.97 for arterioles and 0.95 for venules. The inter-rater ICCs were different (p < 0.01) between the semiautomated and automated version in all instances.
Conclusion: Automated measurements of retinal oximetry values are more repeatable compared to measurements where vessels are selected manually.
Conflict of interest statement
Robert Arnar Karlsson, Sveinn Hakon Hardarson and Einar Stefánsson have commercial interest in the company Oxymap ehf. They have stock in the company, are on its board and are listed on two patents related to retinal oximetry (Automatic registration of images US 7774036 B2, Temporal oximeter WO 2010143208 A3). This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

