The role of L-arginine metabolism in neurocritical care patients
- PMID: 34916417
- PMCID: PMC8771107
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.327331
The role of L-arginine metabolism in neurocritical care patients
Abstract
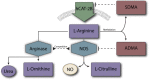
Nitric oxide is an important mediator of vascular autoregulation and is involved in pathophysiological changes after acute neurological disorders. Nitric oxide is generated by nitric oxide synthases from the amino acid L-arginine. L-arginine can also serve as a substrate for arginases or lead to the generation of dimethylarginines, asymmetric dimethylarginine, and symmetric dimethylarginine, by methylation. Asymmetric dimethylarginine is an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase and can lead to endothelial dysfunction. This review discusses the role of L-arginine metabolism in patients suffering from acute and critical neurological disorders often requiring neuro-intensive care treatment. Conditions addressed in this review include intracerebral hemorrhage, aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, and traumatic brain injury. Recent therapeutic advances in the field are described including current randomized controlled trials for traumatic brain injuries and hemorrhagic stroke.
Keywords: arginine; brain injuries; traumatic; cerebral hemorrhage; dimethylarginine; nitric oxide; stroke; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
-
- Ahn M, Lee C, Jung K, Kim H, Moon C, Sim KB, Shin T. Immunohistochemical study of arginase-1 in the spinal cords of rats with clip compression injury. Brain Res. 2012;1445:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Akar E, Emon ST, Uslu S, Orakdogen M, Somay H. Effect of L-Arginine Therapy on Vasospasm: Experimental Study in Rats. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:e443–446. - PubMed
-
- Appel D, Seeberger M, Schwedhelm E, Czorlich P, Goetz AE, Böger RH, Hannemann J. Asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginines are markers of delayed cerebral ischemia and neurological outcome in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. 2018;29:84–93. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

