Thyroid hormone receptor alpha sumoylation modulates white adipose tissue stores
- PMID: 34916557
- PMCID: PMC8677787
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03491-6
Thyroid hormone receptor alpha sumoylation modulates white adipose tissue stores
Abstract
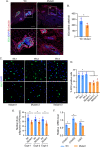
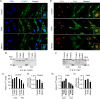
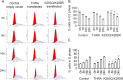
Thyroid hormone (TH) and thyroid hormone receptor (THR) regulate stem cell proliferation and differentiation during development, as well as during tissue renewal and repair in the adult. THR undergoes posttranslational modification by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO). We generated the THRA (K283Q/K288R)-/- mouse model for in vivo studies and used human primary preadipocytes expressing the THRA sumoylation mutant (K283R/K288R) and isolated preadipocytes from mutant mice for in vitro studies. THRA mutant mice had reduced white adipose stores and reduced adipocyte cell diameter on a chow diet, compared to wild-type, and these differences were further enhanced after a high fat diet. Reduced preadipocyte proliferation in mutant mice, compared to wt, was shown after in vivo labeling of preadipocytes with EdU and in preadipocytes isolated from mice fat stores and studied in vitro. Mice with the desumoylated THRA had disruptions in cell cycle G1/S transition and this was associated with a reduction in the availability of cyclin D2 and cyclin-dependent kinase 2. The genes coding for cyclin D1, cyclin D2, cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and Culin3 are stimulated by cAMP Response Element Binding Protein (CREB) and contain CREB Response Elements (CREs) in their regulatory regions. We demonstrate, by Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay, that in mice with the THRA K283Q/K288R mutant there was reduced CREB binding to the CRE. Mice with a THRA sumoylation mutant had reduced fat stores on chow and high fat diets and reduced adipocyte diameter.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone receptor isoform-specific modification by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modulates thyroid hormone-dependent gene regulation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 19;287(43):36499-508. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344317. Epub 2012 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22930759 Free PMC article.
-
Mice lacking the thyroid hormone receptor-alpha gene spend more energy in thermogenesis, burn more fat, and are less sensitive to high-fat diet-induced obesity.Endocrinology. 2008 Dec;149(12):6471-86. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0718. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18719022
-
Type-2 iodothyronine 5'deiodinase (D2) in skeletal muscle of C57Bl/6 mice. II. Evidence for a role of D2 in the hypermetabolism of thyroid hormone receptor alpha-deficient mice.Endocrinology. 2011 Aug;152(8):3093-102. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-0139. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21652727 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a new model of transgenic mice to clarify the respective functions of thyroid hormone receptors in vivo.Heart Fail Rev. 2010 Mar;15(2):117-20. doi: 10.1007/s10741-008-9121-y. Epub 2009 Jan 10. Heart Fail Rev. 2010. PMID: 19137427 Review.
-
Protein sumoylation in brain development, neuronal morphology and spinogenesis.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Dec;15(4):677-91. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8252-z. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23907729 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Sequencing Reveals a Strong Predominance of THRA Splicing Isoform 2 in the Developing and Adult Human Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 13;25(18):9883. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189883. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337374 Free PMC article.
-
TRα2-An Untuned Second Fiddle or Fine-Tuning Thyroid Hormone Action?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 23;23(13):6998. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136998. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

