TREM2 interacts with TDP-43 and mediates microglial neuroprotection against TDP-43-related neurodegeneration
- PMID: 34916658
- PMCID: PMC8741737
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-021-00975-6
TREM2 interacts with TDP-43 and mediates microglial neuroprotection against TDP-43-related neurodegeneration
Abstract
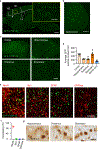
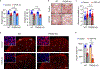
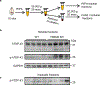
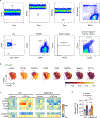
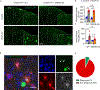
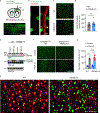
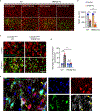
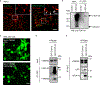
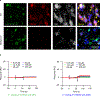
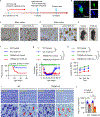
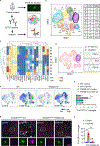
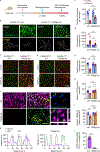
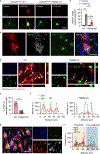
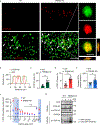
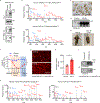
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell 2 (TREM2) is linked to risk of neurodegenerative disease. However, the function of TREM2 in neurodegeneration is still not fully understood. Here, we investigated the role of microglial TREM2 in TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43)-related neurodegeneration using virus-mediated and transgenic mouse models. We found that TREM2 deficiency impaired phagocytic clearance of pathological TDP-43 by microglia and enhanced neuronal damage and motor impairments. Mass cytometry analysis revealed that human TDP-43 (hTDP-43) induced a TREM2-dependent subpopulation of microglia with high CD11c expression and phagocytic ability. Using mass spectrometry (MS) and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis, we further demonstrated an interaction between TDP-43 and TREM2 in vitro and in vivo as well as in human tissues from individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). We computationally identified regions within hTDP-43 that interact with TREM2. Our data highlight that TDP-43 is a possible ligand for microglial TREM2 and that this interaction mediates neuroprotection of microglia in TDP-43-related neurodegeneration.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ulland TK & Colonna M TREM2 - a key player in microglial biology and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 14, 667–675 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

