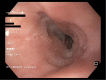
No abstract available
Keywords:
dysphagia; oesophageal disease; oesophageal disorders.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
-
Carmack SW, Vemulapalli R, Spechler SJ, et al. Esophagitis dissecans superficialis ("sloughing esophagitis"): a clinicopathologic study of 12 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1789–94. 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181b7ce21
-
DOI
-
PubMed
-
-
Hart PA, Romano RC, Moreira RK, et al. Esophagitis dissecans superficialis: clinical, endoscopic, and histologic features. Dig Dis Sci 2015;60:2049–57. 10.1007/s10620-015-3590-3
-
DOI
-
PubMed
-
-
Purdy JK, Appelman HD, McKenna BJ. Sloughing esophagitis is associated with chronic debilitation and medications that injure the esophageal mucosa. Mod Pathol 2012;25:767–75. 10.1038/modpathol.2011.204
-
DOI
-
PubMed