Graft and Patient Survival Rates in Kidney Transplantation, and Their Associated Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34917526
- PMCID: PMC8643514
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v50i8.6801
Graft and Patient Survival Rates in Kidney Transplantation, and Their Associated Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) is an irreversible impairment of kidney function that leads to permanently dependent on alternative therapies such as hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and renal transplantation. This study aimed to systematically investigate the survival rate of patients with renal transplantation, graft, and its related factors in Iran.
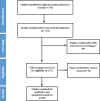
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis drew on articles indexed in six international and one internal databases (Medline/PubMed, ProQuest, Scopus, Embase, SID, and Web of knowledge) until Nov 2020. The reporting of the present study was performed in terms of PRISMA statement. All analyzes were performed using the STATA software.
Results: Overall, 367 titles from 6 databases were evaluated of which 86 articles met the inclusion criteria. According to the random model, the graft survival rate at one, three, five, and 10 years were 92.48%, 85.08%, 79.96% and 68.15% respectively. Additionally, the patient survival rates at one, three, five, and 10 years were 91.27%, 86.46%, 81.17% and 78.15% respectively. There was a significant relationship between the age recipient and three-year graft survival rate (P=0.021). Additionally, there was an inverse and significant relationship between the donor age and 10-year patient survival rate (P=0.011).
Conclusion: The patient and graft survival in transplanted kidney patients is comparable with most developed countries.
Keywords: End stage renal disease; Graft survival; Kidney transplantation; Meta-analysis; Patient survival.
Copyright © 2021 Ghelichi-Ghojogh et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Graft and Patient Survival Rate among Iranian Pediatric Recipients of Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2022 Jun;51(6):1232-1244. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v51i6.9666. Iran J Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36447982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The global survival rate of graft and patient in kidney transplantation of children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2022 Aug 24;22(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12887-022-03545-2. BMC Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36002803 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney and liver organ transplantation in persons with human immunodeficiency virus: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(4):1-56. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074407 Free PMC article.
-
[REIN Report 2011--summary].Nephrol Ther. 2013 Sep;9 Suppl 1:S3-6. doi: 10.1016/S1769-7255(13)70036-1. Nephrol Ther. 2013. PMID: 24119584 French.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical outcomes comparison between different initial dialysis modalities in end-stage renal disease patients due to lupus nephritis prior to renal transplantation.BMC Nephrol. 2020 May 1;21(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01811-y. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32357924 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical profile and outcome of kidney transplantation at Muhimbili National Hospital, Tanzania.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Sep 28;25(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03765-x. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39342167 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide Levels as a Predictor of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Kidney Transplant Recipients.Med Sci Monit. 2025 Feb 4;31:e947197. doi: 10.12659/MSM.947197. Med Sci Monit. 2025. PMID: 39901484 Free PMC article.
-
Graft and Patient Survival Rate among Iranian Pediatric Recipients of Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2022 Jun;51(6):1232-1244. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v51i6.9666. Iran J Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36447982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Donors With Previous Malignancy: When Is It Safe to Proceed With Organ Transplantation?Transpl Int. 2025 Jan 24;38:13716. doi: 10.3389/ti.2025.13716. eCollection 2025. Transpl Int. 2025. PMID: 39926359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peritoneal dialysis vs. hemodialysis among patients with end-stage renal disease in Iran: which is more cost-effective?BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 6;25(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03530-0. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38448887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghelichi Ghojogh M, Taghizadeh Afshari A, et al. (2017). The Effect of Body Mass Index on Patient and Graft Survival Rate in Kidney Transplanted Patients in Iran. Nephro-Urol Mon, 9(4): e14386.
-
- El Nahas AM, Bello AK. (2005). Chronic kidney disease: the global challenge. lancet, 365:331–40. - PubMed
-
- Florit E, Diekmann F, Budde K, et al. (2015). Living Donor Transplantation: Long-Term Evolution Related to Age Matching. Transplantation proceedings, Elsevier, pp. 2346–2350. - PubMed
-
- Einollahi B. (2004). Iranian experience with the non-related renal transplantation. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl, 15:421–428. - PubMed
-
- Jahromi SE, Ahmed F, Pourahmad S, et al. (2019). Predictors of peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis; application of the zero-inflated negative binomial model. J Nephropathol, 8:e36.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous