The effect of treatment with fexofenadine and fluticasone propionate on the gene expression levels of Th9 transcription factors in patients with allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 34917820
- PMCID: PMC8665345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08556
The effect of treatment with fexofenadine and fluticasone propionate on the gene expression levels of Th9 transcription factors in patients with allergic rhinitis
Abstract
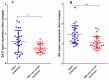
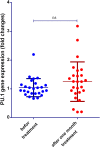
T helper-9 (Th9) is a new T cell subset involved in allergic rhinitis (AR) pathogenesis. Fexofenadine and fluticasone propionate are the first effective line of AR treatment. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of fexofenadine and fluticasone propionate on the gene expression levels of Interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), B cell-activating transcription factor-like (BATF), and SPI1 gene-encoded protein (PU.1), essential transcription factors for Th9 cell differentiation, in AR patients. Twenty-six AR patients (aged 32.8 ± 9.1 years, 13 men and 13 women) were treated with fexofenadine and fluticasone propionate for one month. Expression levels of PU.1, IRF4, and BATF genes were measured using Real-Time PCR. Our results showed that after one month of treatment, the expression level of IRF4 and BATF genes decreased significantly (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, respectively), while PU.1 gene expression was not remarkably different. Overall, our results showed that after one month of treatment with fexofenadine and fluticasone propionate, the expression levels of IRF4 and BATF genes in AR patients decreased, which may be due to this treatment regimen. However, the exact mechanism of action of fexofenadine and fluticasone propionate needs further study.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; BATF; Fexofenadine; Fluticasone propionate; IRF4; PU.1.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bousquet J., Khaltaev N., Cruz A., Denburg J., Fokkens W., Togias A., et al. LEN and AllerGen; 2008. World Health Organization; GA (2) LEN; AllerGen. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 Update. (in collaboration with the world health organization, GA (2) - PubMed
-
- Eiwegger T., Soyka M.B. 2020. Allergic Rhinitis. Pediatric Allergy, E-Book: Principles and Practice; p. 135.
-
- Veldhoen M., Uyttenhove C., Van Snick J., Helmby H., Westendorf A., Buer J., et al. Transforming growth factor-β'reprograms' the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9–producing subset. Nat. Immunol. 2008;9(12):1341–1346. - PubMed
-
- Pilette C., Jacobson M., Ratajczak C., Detry B., Banfield G., VanSnick J., et al. Aberrant dendritic cell function conditions Th2-cell polarization in allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 2013;68(3):312–321. - PubMed
-
- Ciprandi G., De Amici M., Murdaca G., Fenoglio D., Ricciardolo F., Marseglia G., et al. Serum interleukin-17 levels are related to clinical severity in allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 2009;64(9):1375–1378. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

