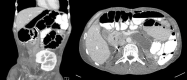
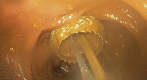
Palliation of malignant distal colonic obstruction via percutaneous endoscopic colostomy using a lumen-apposing metal stent
- PMID: 34917868
- PMCID: PMC8646133
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vgie.2021.09.003
Palliation of malignant distal colonic obstruction via percutaneous endoscopic colostomy using a lumen-apposing metal stent
Abstract
Video 1Palliation of malignant distal colonic obstruction via a percutaneous endoscopic colostomy using a lumen-apposing metal stent.
Keywords: LAMS, lumen-apposing metal stent.
© 2021 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures







Comment in
-
Colostomy using a percutaneous lumen-apposing metal stent.Endoscopy. 2023 Dec;55(S 01):E1131. doi: 10.1055/a-2173-7520. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Endoscopy. 2023. PMID: 37875152 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ramage J.I., Jr., Baron T.H. Percutaneous endoscopic cecostomy: a case series. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:752–755. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

