Efficacy and safety of acupuncture combined Chinese herbal medicine for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34918663
- PMCID: PMC8677943
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028086
Efficacy and safety of acupuncture combined Chinese herbal medicine for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Acupuncture combined with Chinese herbal medicine has been widely utilized for pain management in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). However, its results are still inconsistent, and no systematic review has specifically addressed this issue. Thus, this systematic review will comprehensively and systematically investigate the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture combined with Chinese herbal medicine for pain relief in DPN.
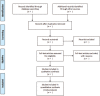
Methods: Randomized controlled trials on acupuncture combined with Chinese herbal medicine treatment of DPN published before September of 2021 will be searched in 9 databases including Medline, Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Excerpta Medica Database, Sinomed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, WanFang, and China Science and Technology Journal Database. The methodological assessment performed using the risk of bias assessment tool of Cochrane, and the level of evidence quality for the main results will be evaluated by a recommended grading, evaluation, formulation, and evaluation system approach. Bayesian network meta-analysis will be conducted using STATA V.14.0 and WinBUGS V.1.4.3.
Results: This study will provide a high-quality comprehensive evaluation of the safety of acupuncture combined with Chinese herbal medicine for treating DPN.
Conclusion: This systematic review will evaluate the efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine combined with acupuncture in the treatment of DPN, and provide the latest evidence for clinical application.
Ethics and dissemination: The protocol of the systematic review does not require ethical approval because it does not involve humans. This article will be published in peer-reviewed journals and presented at relevant conferences.Registration number: INPLASY2021100004.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Similar articles
-
Acupuncture methods for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A protocol for a Bayesian network meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 12;100(10):e24967. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024967. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33725862 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of acupuncture combined with Chinese Herbal Medicine for diabetic nephropathy: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Sep 3;100(35):e27087. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027087. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34477143 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture combine with Tuina for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Dec 3;100(48):e28042. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028042. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 35049219 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: An overview of systematic reviews.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021 Jun;46(3):585-598. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13351. Epub 2021 Jan 28. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021. PMID: 33511675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manual Acupuncture or Combination with Vitamin B to Treat Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Nov 21;2020:4809125. doi: 10.1155/2020/4809125. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33954169 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture and Drug Combination Therapy for Abnormal Glucose Metabolism: Exploring Synergistic Enhancement and Reduced Toxicity Mechanisms.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Nov 28;17:4525-4537. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S492626. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39624791 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, et al. . IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2018;138:271–81. - PubMed
-
- Yang D, Liang X-C. Strategies and research progress of Chinese medicine in prevention and treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Chin J Integr Med 2018;24:794–800. - PubMed
-
- Zhai J, Zhu Y, Pang G, et al. . Clinical observation of 28 cases of astragaloside combined with western medicine in treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Chin J Ethnomed Ethnopharm 2018;101:121–3.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical