The histone H4 lysine 20 demethylase DPY-21 regulates the dynamics of condensin DC binding
- PMID: 34918745
- PMCID: PMC8917352
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.258818
The histone H4 lysine 20 demethylase DPY-21 regulates the dynamics of condensin DC binding
Abstract
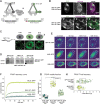
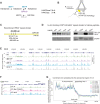
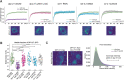
Condensin is a multi-subunit structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) complex that binds to and compacts chromosomes. Here, we addressed the regulation of condensin binding dynamics using Caenorhabditis elegans condensin DC, which represses X chromosomes in hermaphrodites for dosage compensation. We established fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) using the SMC4 homolog DPY-27 and showed that a well-characterized ATPase mutation abolishes DPY-27 binding to X chromosomes. Next, we performed FRAP in the background of several chromatin modifier mutants that cause varying degrees of X chromosome derepression. The greatest effect was in a null mutant of the H4K20me2 demethylase DPY-21, where the mobile fraction of condensin DC reduced from ∼30% to 10%. In contrast, a catalytic mutant of dpy-21 did not regulate condensin DC mobility. Hi-C sequencing data from the dpy-21 null mutant showed little change compared to wild-type data, uncoupling Hi-C-measured long-range DNA contacts from transcriptional repression of the X chromosomes. Taken together, our results indicate that DPY-21 has a non-catalytic role in regulating the dynamics of condensin DC binding, which is important for transcription repression.
Keywords: C. elegans; Condensin; FRAP; Hi-C; Histone modifications; Transcription.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson, E. C., Frankino, P. A., Higuchi-Sanabria, R., Yang, Q., Bian, Q., Podshivalova, K., Shin, A., Kenyon, C., Dillin, A. and Meyer, B. J. (2019). X Chromosome domain architecture regulates caenorhabditis elegans lifespan but not dosage compensation. Dev. Cell 51, 192-207.e6. 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.08.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

