Systematic review of associations between HLA and renal function
- PMID: 34919330
- PMCID: PMC9300076
- DOI: 10.1111/iji.12566
Systematic review of associations between HLA and renal function
Abstract
Introduction: Kidney dysfunction is a highly significant disease, both in the United Kingdom and globally. Many previous studies have reported associations between human leukocyte antigens (HLA) and renal function; this systematic review attempts to identify, summarize and appraise all published studies of these associations.
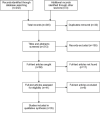
Methods: A literature search was performed using Medline, Embase and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials to identify papers whose keywords included each of the following concepts: HLA, renal failure and genetic association. A total of 245 papers were identified and assessed for eligibility; 35 of these were included in the final study.
Results: A total of 95 HLA types and 14 three-locus haplotypes were reported to be associated with either increased or decreased renal function. A number of these findings were replicated by independent studies that reported 16 types were protective against renal dysfunction and 15 types were associated with reduced renal function. A total of 20 HLA types were associated with both increased risk of renal disease and decreased risk by independent studies.
Discussion: There is very little consensus on which HLA types have a protective or deleterious effect on renal function. Ethnicity may play a role, with HLA types possibly having different effects among different populations, and it is possible that the different primary diseases that lead to ESRD may have different HLA associations. Some of the studies may contain type I and type II errors caused by insufficient sample sizes, cohort selection and statistical methods. Although we have compiled a comprehensive list of published associations between renal function and HLA, in many cases, it is unclear which associations are reliable. Further studies are required to confirm or refute these findings.
Keywords: HLA antigens; chronic; genetic predisposition to disease; genome-wide association study; histocompatibility antigens; kidney failure; renal insufficiency; systematic review.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Immunogenetics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher's disease: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jul;10(24):iii-iv, ix-136. doi: 10.3310/hta10240. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16796930
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
Taxane monotherapy regimens for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD008766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008766.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866378 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
Cited by
-
The Association of Class I and II Human Leukocyte Antigen Serotypes With End-Stage Kidney Disease Due to Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis and Dense Deposit Disease.Am J Kidney Dis. 2024 Jan;83(1):79-89. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.06.005. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024. PMID: 37739026 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison Between Pregabalin and Sertraline in the Treatment of Uremic Pruritus in Patients With Maintenance Hemodialysis.Cureus. 2024 Jul 30;16(7):e65788. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65788. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39211714 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Human Leukocyte Antigen and End-Stage Renal Disease in Patients from Transylvania, Romania.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13383. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713383. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686189 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of HLA Polymorphisms with Chronic Kidney Disease in Japanese Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;14(7):1470. doi: 10.3390/genes14071470. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510374 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DQ and alcohol in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome in college students: a case-control study.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 10;13(1):13023. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40295-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37563425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almogren, A. , Shakoor, Z. , & Hamam, K. D. (2012). Human leucocyte antigens: Their association with end‐stage renal disease in Saudi patients awaiting transplantation. British Journal of Biomedical Science, 69(4), 159–163. - PubMed
-
- Cao, Q. , Xie, D. , Liu, J. , Zou, H. , Zhang, Y. , Zhang, H. , Zhang, Z. , Xue, H. , Zhou, J. , & Chen, P. (2014). HLA polymorphism and susceptibility to end‐stage renal disease in Cantonese patients awaiting kidney transplantation. Plos One, 9(6), e90869. 10.1371/journal.pone.0090869 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials