KRAS mutation-independent downregulation of MAPK/PI3K signaling in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 34919787
- PMCID: PMC8895447
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13163
KRAS mutation-independent downregulation of MAPK/PI3K signaling in colorectal cancer
Abstract
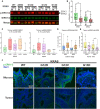
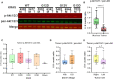
KRAS is a gatekeeper gene in human colorectal tumorigenesis. KRAS is 'undruggable'; hence, efforts have been diverted to inhibit downstream RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling. Nevertheless, none of these inhibitors has progressed to clinical use despite extensive trials. We examined levels of phospho-ERK1/2(T202/Y204) and phospho-Akt1/2/3(S473) in human colorectal tumor compared to matched mucosa with semi-quantitative near-infrared western blot and confocal fluorescence immunohistochemistry imaging. Surprisingly, 75.5% (25/33) of tumors had lower or equivalent phospho-ERK1/2 and 96.9% (31/32) of tumors had lower phospho-Akt1/2/3 compared to matched mucosa, irrespective of KRAS mutation status. In contrast, we discovered KRAS-dependent SOX9 upregulation in 28 of the 31 (90.3%) tumors. These observations were substantiated by analysis of the public domain transcriptomics The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets and proteomics Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC) dataset. These data suggest that RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling are unlikely to be activated in most human colorectal cancer.
Keywords: CPTAC; KRAS signaling; MAPK/PI3K; SOX9; TCGA; colorectal tumorigenesis.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationships among KRAS mutation status, expression of RAS pathway signaling molecules, and clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb 21;25(7):808-823. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.808. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30809081 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases exert dominant control over PI3K signaling in human KRAS mutant colorectal cancers.J Clin Invest. 2011 Nov;121(11):4311-21. doi: 10.1172/JCI57909. Epub 2011 Oct 10. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21985784 Free PMC article.
-
KRAS(G12D)- and BRAF(V600E)-induced transformation of murine pancreatic epithelial cells requires MEK/ERK-stimulated IGF1R signaling.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 Sep;10(9):1228-39. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0340-T. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22871572 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Inhibition of MEK and PI3K Pathway in KRAS and BRAF Mutated Colorectal Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 23;16(9):22976-88. doi: 10.3390/ijms160922976. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26404261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KRAS Pathways: A Potential Gateway for Cancer Therapeutics and Diagnostics.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024;19(3):268-279. doi: 10.2174/1574892818666230406085120. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 37038676 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the 'Undruggable' Driver Protein, KRAS, in Epithelial Cancers: Current Perspective.Cells. 2023 Feb 15;12(4):631. doi: 10.3390/cells12040631. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KRAS-specific antibody binds to KRAS protein inside colorectal adenocarcinoma cells and inhibits its localization to the plasma membrane.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 27;13:1036871. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1036871. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37051535 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Nucleic Acids in Colorectal Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Value.Dis Markers. 2024 Feb 13;2024:9943412. doi: 10.1155/2024/9943412. eCollection 2024. Dis Markers. 2024. PMID: 38380073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAS-targeted cancer therapy: Advances in drugging specific mutations.MedComm (2020). 2023 May 27;4(3):e285. doi: 10.1002/mco2.285. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37250144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epi-nutrients for cancer prevention: Molecular mechanisms and emerging insights.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Jul 15;41(1):116. doi: 10.1007/s10565-025-10054-2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40663150 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Singapore Cancer Registry , Annual Registry Report, Trends in Cancer Incidence in Singapore 2010 – 2014. 2015, National Registry of Diseases Office, Singapore: https://www.nrdo.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider3/default‐document‐library....
-
- Goyle S, Maraveyas A. Chemotherapy for colorectal cancer. Dig Surg. 2005;22:401–14. - PubMed
-
- Bleiberg H. Adjuvant treatment of colon cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2005;17:381–5. - PubMed
-
- Karapetis CS, Khambata‐Ford S, Jonker DJ, O'Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC, et al. K‐ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1757–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

