Rapid characterization of spike variants via mammalian cell surface display
- PMID: 34919820
- PMCID: PMC8675084
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.11.024
Rapid characterization of spike variants via mammalian cell surface display
Abstract
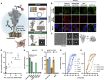
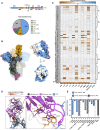
The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is a critical component of vaccines and a target for neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (nAbs). Spike is also undergoing immunogenic selection with variants that increase infectivity and partially escape convalescent plasma. Here, we describe Spike Display, a high-throughput platform to rapidly characterize glycosylated spike ectodomains across multiple coronavirus-family proteins. We assayed ∼200 variant SARS-CoV-2 spikes for their expression, ACE2 binding, and recognition by 13 nAbs. An alanine scan of all five N-terminal domain (NTD) loops highlights a public epitope in the N1, N3, and N5 loops recognized by most NTD-binding nAbs. NTD mutations in variants of concern B.1.1.7 (alpha), B.1.351 (beta), B.1.1.28 (gamma), B.1.427/B.1.429 (epsilon), and B.1.617.2 (delta) impact spike expression and escape most NTD-targeting nAbs. Finally, B.1.351 and B.1.1.28 completely escape a potent ACE2 mimic. We anticipate that Spike Display will accelerate antigen design, deep scanning mutagenesis, and antibody epitope mapping for SARS-CoV-2 and other emerging viral threats.
Keywords: COVID-19; N-terminal domain; cell display; receptor-binding domain; variants.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare competing financial interests. K.J., C.-W.C., H.-C.K., and I.J.F. have filed patent applications on spike-6p (HexaPro). A patent application submitted by The University of Texas Board of Regents is pending for anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies described in the manuscript (W.N.V.). The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare no competing non-financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Andreano E., Piccini G., Licastro D., Casalino L., Johnson N.V., Paciello I., Dal Monego S., Pantano E., Manganaro N., Manenti A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 escape from a highly neutralizing COVID-19 convalescent plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2021;118 doi: 10.1073/pnas.2103154118. e2103154118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

