mRNA intramuscular vaccination produces a robust IgG antibody response in advanced neuromuscular disease
- PMID: 34920929
- PMCID: PMC8603918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2021.11.006
mRNA intramuscular vaccination produces a robust IgG antibody response in advanced neuromuscular disease
Abstract
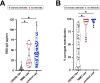
SARS-CoV-2 vaccines protect against symptomatic and severe COVID-19. The BNT162b2/Pfizer and mRNA-1273/Moderna vaccines represent new vaccine technology relying on administration of mRNA encoding SARS-CoV-2 viral spike protein encased in lipid nanoparticles. The vaccines are administered as two doses into muscle, which elicits a strong response, typically within 14 days after the second dose. Neuromuscular diseases are characterized by the progressive loss of muscle and are often treated with chronic glucocorticoid steroids, both of which may contribute to a blunted immune response to vaccination. Here, we measured IgG antibody content and neutralizing antibody response after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in non-ambulatory neuromuscular disease patients. After two doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, median anti-receptor binding domain IgG and percent surrogate viral neutralization in non-ambulatory neuromuscular disease samples were significantly elevated similar to healthy vaccinated controls. As in healthy controls, COVID-19 vaccines produce greater antibody levels compared to those with a history of outpatient COVID-19 infection. This data documents that non-ambulatory neuromuscular disease patients respond well to two doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine despite low muscle mass and even chronic steroid use.
Keywords: COVID-19; Dried blood spots; ELISA; IgG; Muscular dystrophy; Neuromuscular; Receptor binding domain; SARS-CoV-2; Serological testing.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Thomas McDade has a financial interest in EnMed Microanalytics, a company that specializes in laboratory testing of dried blood spot samples. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Comment in
-
Safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines in people with neurological disorders.Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Feb;18(2):66. doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00603-8. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34887547 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Khoury D.S., Cromer D., Reynaldi A., Schlub T.E., Wheatley A.K., Juno J.A., et al. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med. 2021;27:1205–1211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

