Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Pharmacodynamics of Romiplostim in Chinese Subjects With Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Phase I/II Trial
- PMID: 34921514
- PMCID: PMC9299913
- DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.1059
Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Pharmacodynamics of Romiplostim in Chinese Subjects With Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Phase I/II Trial
Abstract
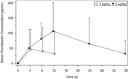
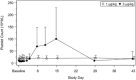
Romiplostim is approved for the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). This study aimed to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety, and pharmacodynamics of romiplostim in Chinese patients with ITP. This multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation phase I/II trial enrolled ITP patients from 5 centers in China between October 2015 and August 2017. There were 2 cohorts: 1 μg/kg and 3 μg/kg weekly for 2 weeks. The end points included pharmacokinetics, platelet changes from baseline, hematological indicators, and adverse events (AEs). Sixteen participants, with 8 patients in each cohort, were enrolled. In the 1 μg/kg cohort, time to maximum concentration was 4.00 (4.00-7.83) hours, maximum serum drug concentration was 52.0 (16.0-228.0) pg/mL, and area under the serum drug concentration-time curve from time 0 to the last detectable time point was 389 (32.0-5400) pg · h/mL. In the 3 μg/kg cohort, time to maximum serum drug concentration was 11.91 (4.00-12.00) hours, maximum serum drug concentration was 105.0 (25.5-313.0) pg/mL, and half-life was 12.7 (8.2-23.6) hours. The absolute change of peak platelet count from baseline was 14 (3-40) and 72 (3-369) ×109 /L in the 1 and 3 μg/kg cohorts, respectively. Seven (87.5%) and eight (100%) participants had treatment-emergent AEs in 1 μg/kg cohort and 3 μg/kg cohort, respectively. No major AEs occurred in the 2 cohorts. Romiplostim (1 and 3 μg/kg) is safe and well tolerated in Chinese patients with ITP.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02868060.
Keywords: immune thrombocytopenia; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; phase I/II; romiplostim; safety.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term use of the thrombopoietin-mimetic romiplostim in children with severe chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015 Feb;62(2):208-213. doi: 10.1002/pbc.25136. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25345874 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A single-arm, long-term efficacy and safety study of subcutaneous romiplostim in children with immune thrombocytopenia.Blood Adv. 2023 Feb 14;7(3):396-405. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006014. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 35413092 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II, open-label, sequential-cohort, dose-escalation study of romiplostim in Japanese patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura.Int J Hematol. 2009 Sep;90(2):157-165. doi: 10.1007/s12185-009-0361-y. Epub 2009 Jun 20. Int J Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19543952 Clinical Trial.
-
Romiplostim in chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura.Clin Ther. 2009 Sep;31(9):1887-907. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.09.013. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19843480 Review.
-
Romiplostim: a review of its use in immune thrombocytopenia.Drugs. 2012 Feb 12;72(3):415-35. doi: 10.2165/11208260-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22316355 Review.
Cited by
-
Romiplostim in primary immune thrombocytopenia that is persistent or chronic: phase III multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial in China.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023 May 23;7(5):100192. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.100192. eCollection 2023 Jul. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 37601010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cines DB, Blanchette VS. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. New Engl J Med. 2002;346(13):995‐1008. - PubMed
-
- Psaila B, Bussel JB. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Hematol/Oncol Clin North Am. 2007;21(4):743‐759, vii. - PubMed
-
- Al‐Samkari H, Kuter DJ. Immune thrombocytopenia in adults: modern approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020;46(3):275‐288. - PubMed
-
- Neunert C, Lim W, Crowther M, et al. The American Society of Hematology 2011 evidence‐based practice guideline for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2011;117(16):4190‐4207. - PubMed
-
- Cooper N, Ghanima W. Immune thrombocytopenia. New Engl J Med. 2019;381(10):945‐955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical