TM4SF5-mediated liver malignancy involves NK cell exhaustion-like phenotypes
- PMID: 34921636
- PMCID: PMC8739317
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-021-04051-x
TM4SF5-mediated liver malignancy involves NK cell exhaustion-like phenotypes
Abstract
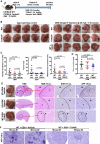
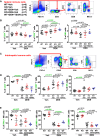
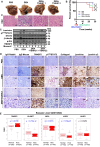
Aberrant extracellular matrix and immune cell alterations within the tumor microenvironment promote the pathological progression of liver carcinogenesis. Although transmembrane 4 L six family member 5 (TM4SF5) is involved in liver fibrosis and cancer, its mechanism avoiding immune surveillance during carcinogenesis remains unknown. We investigated how TM4SF5-mediated signaling caused immune evasion using in vitro primary cells and in vivo liver tissues from genetic or chemically induced mouse models. TM4SF5-transgenic and diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced liver cancer mouse models exhibited fibrotic and cancerous livers, respectively, with enhanced TM4SF5, pY705STAT3, collagen I, and laminin γ2 levels. These TM4SF5-mediated effects were abolished by TM4SF5 inhibitor, 4'-(p-toluenesulfonylamido)-4-hydroxychalcone (TSAHC). TM4SF5-dependent tumorigenesis involved natural killer (NK) cell exhaustion-like phenotypes including the reduction of NK cell number or function, which were blocked with TSAHC treatment. TM4SF5 expression in cancer cells downregulated stimulatory ligands and receptors for NK cell cytotoxicity, including SLAMF6, SLAMF7, MICA/B, and others. TM4SF5 suppression or inhibition reduced STAT3 signaling activity and recovered the receptor levels and NK cell surveillance, leading to reduced fibrotic and cancerous phenotypes, and longer survival. Altogether, these findings suggest that TM4SF5-mediated STAT3 activity for extracellular matrix modulation is involved in the progression of liver disease to HCC and that TM4SF5 appears to suppress NK cells during liver carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Immune checkpoint; L6 family member; Liver cancer; NK cell immune therapy; Signal transduction.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Isoxazole-based molecules restore NK cell immune surveillance in hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting TM4SF5 and SLAMF7 linkage.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jan 20;10(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02106-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39828766 Free PMC article.
-
Differential TM4SF5-mediated SIRT1 modulation and metabolic signaling in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis progression.J Pathol. 2021 Jan;253(1):55-67. doi: 10.1002/path.5548. Epub 2020 Oct 22. J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32918742
-
Blockade of four-transmembrane L6 family member 5 (TM4SF5)-mediated tumorigenicity in hepatocytes by a synthetic chalcone derivative.Hepatology. 2009 Apr;49(4):1316-25. doi: 10.1002/hep.22777. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19177595
-
TM4SF5-Mediated Roles in the Development of Fibrotic Phenotypes.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:5108525. doi: 10.1155/2017/5108525. Epub 2017 Mar 26. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28458469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Killer Cell Dysfunction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Pathogenesis and Clinical Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 19;19(11):3648. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113648. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30463262 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional crosstalk and regulation of natural killer cells in tumor microenvironment: Significance and potential therapeutic strategies.Genes Dis. 2022 Aug 6;10(3):990-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.07.009. eCollection 2023 May. Genes Dis. 2022. PMID: 37396514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver-originated small extracellular vesicles with TM4SF5 target brown adipose tissue for homeostatic glucose clearance.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 Sep;11(9):e12262. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12262. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022. PMID: 36063136 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-specific deletion of miR-181ab1 reduces liver tumour progression via upregulation of CBX7.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 22;79(8):443. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04452-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35867177 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-mediated mitochondrial reprogramming by cholesterol export at TM4SF5-enriched mitochondria-lysosome contact sites.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2024 Jan;44(1):47-75. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12510. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38133457 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic TM4SF5 overexpression in ApcMin/+ mice promotes hepatic portal hypertension associated with fibrosis.BMB Rep. 2022 Dec;55(12):609-614. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2022.55.12.104. BMB Rep. 2022. PMID: 36104259 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

