piRNAs initiate transcriptional silencing of spermatogenic genes during C. elegans germline development
- PMID: 34921763
- PMCID: PMC8796119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.11.025
piRNAs initiate transcriptional silencing of spermatogenic genes during C. elegans germline development
Abstract
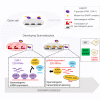
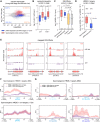
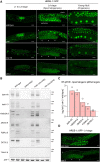
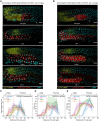
Eukaryotic genomes harbor invading transposable elements that are silenced by PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) to maintain genome integrity in animal germ cells. However, whether piRNAs also regulate endogenous gene expression programs remains unclear. Here, we show that C. elegans piRNAs trigger the transcriptional silencing of hundreds of spermatogenic genes during spermatogenesis, promoting sperm differentiation and function. This silencing signal requires piRNA-dependent small RNA biogenesis and loading into downstream nuclear effectors, which correlates with the dynamic reorganization of two distinct perinuclear biomolecular condensates present in germ cells. In addition, the silencing capacity of piRNAs is temporally counteracted by the Argonaute CSR-1, which targets and licenses spermatogenic gene transcription. The spatial and temporal overlap between these opposing small RNA pathways contributes to setting up the timing of the spermatogenic differentiation program. Thus, our work identifies a prominent role for piRNAs as direct regulators of endogenous transcriptional programs during germline development and gamete differentiation.
Keywords: C. elegans; RNAi; epigenetics; fertility; germ granules; germline development; piRNAs; small RNAs; spermatogenesis; transcriptional silencing.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
PIWI puts spermatogenesis in its place.Dev Cell. 2022 Jan 24;57(2):149-151. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.01.001. Dev Cell. 2022. PMID: 35077678
References
-
- Aravin A., Gaidatzis D., Pfeffer S., Lagos-Quintana M., Landgraf P., Iovino N., Morris P., Brownstein M.J., Kuramochi-Miyagawa S., Nakano T., et al. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature. 2006;442:203–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

