The ECHELON-2 Trial: 5-year results of a randomized, phase III study of brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 34921960
- PMCID: PMC9447792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.12.002
The ECHELON-2 Trial: 5-year results of a randomized, phase III study of brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: For patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), outcomes using frontline treatment with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) or CHOP-like therapy are typically poor. The ECHELON-2 study demonstrated that brentuximab vedotin plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (A+CHP) exhibited statistically superior progression-free survival (PFS) per independent central review and improvements in overall survival versus CHOP for the frontline treatment of patients with systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma or other CD30-positive PTCL.
Patients and methods: ECHELON-2 is a double-blind, double-dummy, randomized, placebo-controlled, active-comparator phase III study. We present an exploratory update of the ECHELON-2 study, including an analysis of 5-year PFS per investigator in the intent-to-treat analysis group.
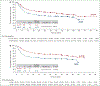
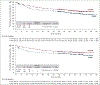
Results: A total of 452 patients were randomized (1 : 1) to six or eight cycles of A+CHP (N = 226) or CHOP (N = 226). At median follow-up of 47.6 months, 5-year PFS rates were 51.4% [95% confidence interval (CI): 42.8% to 59.4%] with A+CHP versus 43.0% (95% CI: 35.8% to 50.0%) with CHOP (hazard ratio = 0.70; 95% CI: 0.53-0.91), and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were 70.1% (95% CI: 63.3% to 75.9%) with A+CHP versus 61.0% (95% CI: 54.0% to 67.3%) with CHOP (hazard ratio = 0.72; 95% CI: 0.53-0.99). Both PFS and OS were generally consistent across key subgroups. Peripheral neuropathy was resolved or improved in 72% (84/117) of patients in the A+CHP arm and 78% (97/124) in the CHOP arm. Among patients who relapsed and subsequently received brentuximab vedotin, the objective response rate was 59% with brentuximab vedotin retreatment after A+CHP and 50% with subsequent brentuximab vedotin after CHOP.
Conclusions: In this 5-year update of ECHELON-2, frontline treatment of patients with PTCL with A+CHP continues to provide clinically meaningful improvement in PFS and OS versus CHOP, with a manageable safety profile, including continued resolution or improvement of peripheral neuropathy.
Keywords: CHOP; brentuximab vedotin; frontline treatment; overall survival; peripheral T-cell lymphoma; randomized clinical trial.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure SH reports receiving research support from ADC Therapeutics, Affimed, Aileron, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Forty Seven, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Millennium/Takeda, Seagen, Trillium Therapeutics, and Verastem/Secura Bio; and consulting for Acrotech Biopharma, ADC Therapeutics, Astex, C4 Therapeutics, Celgene, Janssen, Kura Oncology, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Myeloid Therapeutics, ONO Pharmaceuticals, Seagen, Secura Bio, Shoreline Biosciences, Takeda, Trillium Therapeutics, Tubulis, Verastem, and Vividion Therapeutics. OAO reports advisory membership for Mundipharma, Kymera, Dren Bio, Myeloid Therapeutics, NomoCan; corporate board membership for NomoCan; consultancy for Mundipharma, Servier, Ping; employment with TG therapeutics; equity ownership of TG Therapeutics, Myeloid Therapeutics, Kymera, NomoCan, Dren Bio; honoraria from Mundipharma, Servier, and Pint; research funding from Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS)/Celgene, Astex, Kymera; and travel expenses from Mundipharma, Servier, and TG Therapeutics. BP reports consultancy, honoraria, research funding, and travel expenses for Seagen; and honoraria and travel expenses for Takeda. LT reports consultancy for Janssen, Nordic Nanovector, and Takeda Europe; and research funding from Mundipharma, Roche, Seagen, and Takeda Europe. SI reports receiving research funding from Seagen, Merck, CRISPRx, Innate, Affimed, Rhizen, Spectrum, Trillium, and Cellectis; and honoraria from Targeted Oncology and Curio Science. RA reports consultancy for AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Celgene, Cell Medica, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, Kite Pharma, Kyowa, Portola Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Seagen, and Takeda; and research funding from Celgene, Forty Seven, Genentech/Roche, Janssen Pharma, Kura, Merck, Millenium, Pharmacyclics, Regeneron, and Seagen. NLB reports advisory boards for ADC Therapeutics, Roche/Genentech, and Seagen; and research funding from ADC Therapeutics, Affimed, Autolus, BMS, Celgene, Forty Seven, Janssen, Kite Pharma, Merck, Millennium, Pharmacyclics, Roche/Genentech, and Seagen. FM reports advisory board membership for AbbVie, Celgene/BMS, Epizyme, Gilead, Roche; consultancy for Gilead, Roche, Servier; and honoraria from Janssen and Roche. ED-D reports advisory board and corporate board membership for Takeda, and travel expenses for BMS, Roche, and Takeda. GR reports advisory board membership for AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Jazz, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Teva; honoraria from BMS, Daiichi, Mundipharma, Novartis, Sandoz; research funding from Seagen; and travel expenses from Alexion, Celgene, and Gilead. WSK reports receiving research funding/grants from Celltrion, Donga, Johnson & Johnson, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Mundipharma, Pfizer, Roche, Seagen, and Takeda. TF reports advisory board membership for Bayer, BMS, Seagen, consultancy for AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Kyowa Kirin, MorphoSys, Seagen; honoraria for AbbVie, Bayer, BMS, Kite Pharma, Pharmacyclics, Seagen, Takeda; research funding for Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Cell Medica, Corvus, Eisai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Pfizer, Portola Pharma, Roche, Seagen, Trillium, Viracta; speaker's bureau for AbbVie, Celgene, Janssen, Kite Pharma, Pharmacyclics, Seagen; and travel expenses for AbbVie, Kite Pharma, Pharmacyclics, Seagen, Takeda. TM reports receiving honoraria from Amgen, Atara, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Takeda; research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen, and Novartis, and travel expenses from Amgen, Bayer, Celgene, Jazz, Kite/Gilead, Kyowa Kirin, and Pfizer. DB reports advisory board membership for Gilead and Roche; consultancy for Gilead, Janssen, and Roche; research funding from Celgene, Janssen, Roche, and Takeda; and travel expenses from Gilead and Roche. ÁI reports advisory board membership and corporate board membership for Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Roche, and Takeda; research funding from Seagen and Takeda; and travel expenses from Roche and Takeda. KTo reports consultancy for Celgene, Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, HUYA Bioscience International, Kyowa Kirin, Mundipharma, Ono Pharmaceutical, SymBio, Takeda, Yakult, and Zenyaku Kogyo; and honoraria from BMS-Celgene, Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, HUYA Bioscience International, Kyowa Kirin, Mundipharma, Ono Pharma, Solasia Pharma, Takeda, Yakult, and Zenyaku Kogyo. KTs reports consultancy for Daiichi Sankyo, HUYA, Ono Pharma, Meiji Seika Pharma, and Yakuruto; honoraria from Celgene, Chugai Pharma, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, and Mundy Pharma; research funding from Chugai Pharma, Eisai, HUYA, Seagen, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Byer, Celgene, and Daiichi-Sankyo. S-PY reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Astellas, Astex, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda. AS reports consulting for Acrotech, BMS-Celgene, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, TG Therapeutics, and Verastem. AH reports receiving research funding from Seagen and travel expenses from Celgene and Roche. KS reports consultancy for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Gilead, Merck, Seagen, Servier, Kyowa, Novartis Canada; honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Gilead, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, Novartis, Novartis Canada Pharma, Seagen; research funding from BMS, Roche; and travel expenses from Seagen. SY reports receiving research funding and travel expenses from Seagen. PLZ reports advisory board membership with AbbVie, Gilead, Incyte, Merck, Portola, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, and Takeda; consultancy for BMS, Celgene, Celltron, Eusapharma, Gilead, Immune Design, Janssen-Cilag, Kyowa Kirin, Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), Roche, Sandoz, Verastem; honoraria from AbbVie, ADC Therapeutics, BMS, Debiopharm, EUSA Pharma, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, Roche, Servier, Takeda, TG Therapeutics, Verastem; research funding from Portola; and speaker's bureau for AbbVie, ADC Therapeutics, BMS, Celgene, Celltron, EUSA Pharma, Gilead, Immune Design, Incyte, Janssen, Janssen-Cilag, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, MSD, Portola, Roche, Sandoz, Servier, Takeda, TG Therapeutics, and Verastem. HM and VB report employment for Takeda. KF, MF, and MP report being employed by and holding shares in Seagen. TI reports advisory board membership and speaker's bureau for Takeda. All other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D, International T-Cell lymphoma project. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4124–4130. - PubMed
-
- Savage KJ, Harris NL, Vose JM, et al. ALK- anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is clinically and immunophenotypically different from both ALK+ ALCL and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: report from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood. 2008;111:5496–5504. - PubMed
-
- Ellin F, Landstrom J, Jerkeman M, Relander T. Real-world data on prognostic factors and treatment in peripheral T-cell lymphomas: a study from the Swedish Lymphoma Registry. Blood. 2014;124:1570–1577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

