Del Nido versus HTK cardioplegia for myocardial protection during adult complex valve surgery: a retrospective study
- PMID: 34922443
- PMCID: PMC8683821
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-021-02411-w
Del Nido versus HTK cardioplegia for myocardial protection during adult complex valve surgery: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate (HTK) and del Nido (DN) cardioplegia are intracellular-type and extracellular-type solution respectively, both can provide a long period of myocardial protection with single-dose infusion, but studies comparing the two are rare for adult cardiac surgery. This study aims to evaluate whether DN is suitable for cardioplegia in complex and high-risk valve surgery with long-term cardiac ischemia when compared with HTK.
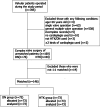
Methods: The perioperative records of adult patients infused with DN/HTK as a cardioplegic solution who underwent complex valve surgery with an expected myocardial ischaemic duration longer than 90 min between Oct 2018 and Oct 2019 were analysed retrospectively.
Results: Of the 160 patients who received DN/HTK and underwent complex valve surgery, we propensity matched 73 pairs. Both groups achieved satisfactory cardiac arrest effects, and no significant difference was found in their cTnI and CK-MB levels within 12 to 72 h postoperatively. The DN group had a higher rate of return to spontaneous rhythm (0.88 v 0.52, P < 0.001), a lower frequency of postoperative severe arrythmias (12% v 26%, P = 0.036), a higher postoperative stroke volume (65 v 59 ml, P = 0.011) and a higher cardiac output (6.0 v 4.9 L/min, P = 0.007) as evaluated by echocardiography, fewer transfusions and shorter ICU stays (both P < 0.05). The two groups had similar inotrope usage and similar incidences of low cardiac output, morbidities and mortality. Subgroup analysis showed that when the aortic clamping time was greater than 120 min, the advantages of DN were weakened.
Conclusions: DN can be safely applied to complex valve surgery, and it has a similar myocardial protection effect as HTK. Further prospective studies are required to verify these retrospective findings. Trial registration retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Economic; ICU stay; Myocardial protection; Return to spontaneous rhythm; Single-dose cardioplegia.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transitioning to Del Nido cardioplegia for all-comers: the next switching gear?BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 May 8;20(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01506-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32384925 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Myocardial Protection in Prolonged Aortic Cross-Clamp Times: Del Nido and HTK Cardioplegia in Adult Cardiac Surgery.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Aug 6;61(8):1420. doi: 10.3390/medicina61081420. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40870465 Free PMC article.
-
Del Nido cardioplegia versus blood cardioplegia in adult aortic root surgery.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021 Aug;162(2):514-522.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.01.022. Epub 2020 Jan 30. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 32111432
-
Recent advances in Del Nido cardioplegia: A comprehensive analysis of randomized clinical trials in adult cardiac surgery.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 6;103(36):e39453. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039453. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39252294 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of del Nido Cardioplegia on Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Study-level Meta-analysis.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2025 Jun;39(6):1538-1546. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2025.01.007. Epub 2025 Jan 13. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2025. PMID: 39909765 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of fibrinogen albumin ratio in patients with pregnancy-related cerebral venous thrombosis.Acta Neurol Belg. 2023 Dec;123(6):2251-2258. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02294-y. Epub 2023 May 22. Acta Neurol Belg. 2023. PMID: 37217742
-
Comparison of Single-Dose Cardioplegia in Valvular Heart Surgery: Lactated Ringer's-Based del Nido vs. Histidine-Tryptophan-Ketoglutarate Cardioplegia Solution.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2023 Oct 6;38(6):e20220447. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2022-0447. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 37801520 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the efficacy between Del Nido cardioplegia and HTK cardioplegia in Stanford type A aortic dissection patients undergoing open-heart surgery.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Sep 28;47(9):1235-1243. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.220217. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36411707 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
The cardioprotective effects of HTK solution and conventional blood cardioplegia in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing valvular replacement and Cox maze III procedure.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 Jan 6;20(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-03317-2. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 39757216 Free PMC article.
-
Non-selective Del Nido and St Thomas cardioplegia in adults: analysis of early clinical experience using propensity matching.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2023 Jan-Dec;17:17539447231210713. doi: 10.1177/17539447231210713. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 37991005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gorjipour F, Dehaki MG, Totonchi Z, Hajimiresmaiel SJ, Azarfarin R, Pazoki-toroudi H, et al. Inflammatory cytokine response and cardiac troponin I changes in cardiopulmonary bypass using two cardioplegia solutions; del Nido and modified St. Thomas’: a randomized controlled trial. Perfusion. 2017;32(5):394–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

