Glyoxal damages human aortic endothelial cells by perturbing the glutathione, mitochondrial membrane potential, and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways
- PMID: 34922451
- PMCID: PMC8684178
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-021-02418-3
Glyoxal damages human aortic endothelial cells by perturbing the glutathione, mitochondrial membrane potential, and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways
Abstract
Background: Exposure to glyoxal, the smallest dialdehyde, is associated with several diseases; humans are routinely exposed to glyoxal because of its ubiquitous presence in foods and the environment. The aim of this study was to examine the damage caused by glyoxal in human aortic endothelial cells.
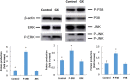
Methods: Cell survival assays and quantitative fluorescence assays were performed to measure DNA damage; oxidative stress was detected by colorimetric assays and quantitative fluorescence, and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways were assessed using western blotting.
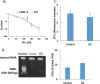
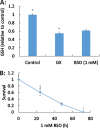
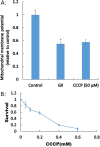
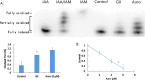
Results: Exposure to glyoxal was found to be linked to abnormal glutathione activity, the collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential, and the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. However, DNA damage and thioredoxin oxidation were not induced by dialdehydes.
Conclusions: Intracellular glutathione, members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, and the mitochondrial membrane potential are all critical targets of glyoxal. These findings provide novel insights into the molecular mechanisms perturbed by glyoxal, and may facilitate the development of new therapeutics and diagnostic markers for cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Glyoxal; Human aortic endothelial cells; Laboratory indexes; Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
H2O2-dependent activation of GCLC-ARE4 reporter occurs by mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways without oxidation of cellular glutathione or thioredoxin-1.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 13;279(7):5837-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307547200. Epub 2003 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14638694
-
Lovastatin attenuates glyoxal-induced toxicity on rat liver mitochondria.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Dec;40(12):2215-2222. doi: 10.1177/09603271211027939. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34165024
-
D-chiro-inositol enriched Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaench extract alleviates mitochondrial malfunction and inhibits ER stress/JNK associated inflammation in the endothelium.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 25;214:83-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29225119
-
Retinol binding protein 4 induces mitochondrial dysfunction and vascular oxidative damage.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Jun;240(2):335-44. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.03.036. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 25875385
-
Redox control of cell death.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Jun;4(3):405-14. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196209. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. PMID: 12215208 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics-based evaluation of the mechanism underlying vascular injury via DNA interstrand crosslinks, glutathione perturbation, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and Wnt and ErbB signaling pathways induced by crotonaldehyde.Clin Proteomics. 2022 Aug 24;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12014-022-09369-7. Clin Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 36002804 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Glyoxal on Plasma Membrane and Cytosolic Proteins of Erythrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 2;26(9):4328. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094328. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362565 Free PMC article.
-
Association between redox biomarkers, DNA damage and aerobic capacity before and after physical stress in young men.Redox Biol. 2025 Jul 10;85:103764. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103764. Online ahead of print. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40651083 Free PMC article.
-
Glyoxal in hyperglycaemic ischemic stroke - a cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jul 12;22(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01892-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37438755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zarzana KJ, Min KE, Washenfelder RA, Kaiser J, Krawiec-Thayer M, Peischl J, Neuman JA, Nowak JB. Emissions of glyoxal and other carbonyl compounds from agricultural biomass burning plumes sampled by aircraft. Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51(20):11761–11770. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b03517. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

