Anorexia nervosa, conduct disorder, and the juvenile justice system: a case of applying traditional treatment modalities in a non-traditional setting
- PMID: 34922570
- PMCID: PMC8684194
- DOI: 10.1186/s13030-021-00227-w
Anorexia nervosa, conduct disorder, and the juvenile justice system: a case of applying traditional treatment modalities in a non-traditional setting
Abstract
Background: Anorexia Nervosa is highly comorbid with depressive, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorders. However, it has not previously been reported as comorbid with antisocial personality traits, except when substance use disorder is also identified. We present an unusual case of a patient with resistant anorexia nervosa and comorbid conduct disorder. This case was also unique in that the juvenile justice system was involved during treatment.
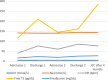
Case presentation: A 13-year-old female was admitted to our pediatric hospital for the treatment of anorexia nervosa. She had a history of violent behaviors toward family members, often jeopardizing her care. During hospitalization, she physically attacked a physician on her care team shortly before she transitioned to an eating disorders treatment program. She was diagnosed with conduct disorder, and following discharge, she attacked her father in a premeditated act. This led to her entry into the juvenile justice system. While under the custody of the juvenile justice system, she was readmitted to our hospital for further treatment of anorexia nervosa. Our treatment strategy included psychotropics, positive reinforcement, close interdisciplinary coordination among the various hospital teams, and the juvenile justice system. Following discharge from her second hospitalization back to the juvenile detention system, our patient maintained a healthy weight and appeared to show improvements in the cognitive distortions related to her eating disorder.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first reported successful treatment of an individual with resistant anorexia nervosa and conduct disorder. It was likely a combination of weight gain, psychotropic medications, and the structured milieu provided by the juvenile justice system that led to the effective treatment of our patient. This case illustrates that a non-traditional healthcare setting can be an asset to treatment through persistence and close collaboration across institutions.
Keywords: Anorexia; Antisocial; Conduct; Interdisciplinary; Justice; Juvenile; Non-traditional; Personality.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Applying integrated enhanced cognitive behaviour therapy (I-CBTE) to severe and longstanding eating disorders (SEED) Paper 2: An in-depth case study for clinicians.J Eat Disord. 2024 Oct 31;12(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s40337-024-01116-7. J Eat Disord. 2024. PMID: 39482743 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement in depressive symptoms in a patient with severe and enduring anorexia nervosa and comorbid major depressive disorder using psychotherapy-assisted IV ketamine : a case report.J Eat Disord. 2024 Jun 12;12(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40337-024-01039-3. J Eat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38867336 Free PMC article.
-
[The psychiatric comorbidity of anorexia nervosa: A comparative study in a population of French and Greek anorexic patients].Encephale. 2018 Nov;44(5):429-434. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2017.07.005. Encephale. 2018. PMID: 29102367 French.
-
Anorexia Nervosa and Comorbid Psychopathology.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2018;18(4):316-324. doi: 10.2174/1871530318666180213111637. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29437020 Review.
-
Predisposition factors in anorexia nervosa.Adolescence. 1992 Summer;27(106):381-6. Adolescence. 1992. PMID: 1621568 Review.
References
-
- Swanson SA, Crow SJ, Le Grange D, Swendsen J, Merikangas KR. Prevalence and correlates of eating disorders in adolescents. Results from the national comorbidity survey replication adolescent supplement. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68(7):714–723. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.22. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources