Phenotypic whole-cell screening identifies a protective carbohydrate epitope on Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 34923908
- PMCID: PMC8726669
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2021.2006123
Phenotypic whole-cell screening identifies a protective carbohydrate epitope on Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
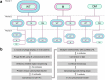
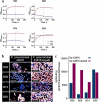
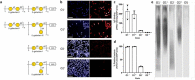
The increasing global occurrence of recalcitrant multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections warrants the investigation of alternative therapy options, such as the use of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). We used a target-agnostic phage display approach to K. pneumoniae bacteria lacking bulky, highly variable surface polysaccharides in order to isolate antibodies targeting conserved epitopes among clinically relevant strains. One antibody population contained a high proportion of unique carbohydrate binders, and biolayer interferometry revealed these antibodies bound to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Antibodies that bound to O1 and O1/O2 LPS were identified. Antibodies were found to promote opsonophagocytic killing by human monocyte-derived macrophages and clearance of macrophage-associated bacteria when assessed using high-content imaging. One antibody, B39, was found to protect mice in a lethal model of K. pneumoniae pneumonia against both O1 and O2 strains when dosed therapeutically. High-content imaging, western blotting and fluorescence-activated cell sorting were used to determine binding to a collection of clinical K. pneumoniae O1 and O2 strains. The data suggests B39 binds to D-galactan-I and D-galactan-II of the LPS of O1 and O2 strains. Thus, we have discovered an mAb with novel binding and functional activity properties that is a promising candidate for development as a novel biotherapeutic for the treatment and prevention of K. pneumoniae infections.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; Phage display; antimicrobial resistance; lipopolysaccharide; monoclonal antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
SR, RM, LI, CC, PW, and DT are current/former employees of the AstraZeneca Group and may have/had stock options in AstraZeneca.
Figures





References
-
- Friedlaender C. Ueber die Schizomyceten bei der acuten fibrösen Pneumonie. Arch für Pathol Anat und Physiol und für Klin Med. 1882;87:319–13.
-
- Rock C, Thom KA, Masnick M, Johnson JK, Harris AD, Morgan DJ. Frequency of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)–producing and non-KPC-producing Klebsiella species contamination of healthcare workers and the environment. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol Off J Soc Hosp Epidemiol Am. 2014;35(4):426. doi: 10.1086/675598. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee C-R, Lee JH, Park KS, Jeon JH, Kim YB, Cha C-J, Jeong BC, Lee SH. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:483. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00483. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
