Association of APOE ɛ4 and Plasma p-tau181 with Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease and Longitudinal Change in Hippocampus Function
- PMID: 34924376
- PMCID: PMC8925119
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-210673
Association of APOE ɛ4 and Plasma p-tau181 with Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease and Longitudinal Change in Hippocampus Function
Abstract
Background: The Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ɛ4 allele has been linked to increased tau phosphorylation and tangle formation. APOE ɛ4 carriers with elevated tau might be at the higher risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD) progression. Previous studies showed that tau pathology begins early in areas of the medial temporal lobe. Similarly, APOE ɛ4 carriers showed altered hippocampal functional integrity. However, it remains unknown whether the influence of elevated tau accumulation on hippocampal functional changes would be more pronounced for APOE ɛ4 carriers.
Objective: We related ɛ4 carriage to levels of plasma phosphorylated tau (p-tau181) up to 15 years prior to AD onset. Furthermore, elevated p-tau181 was explored in relation to longitudinal changes in hippocampal function and connectivity.
Methods: Plasma p-tau181 was analyzed in 142 clinically defined AD cases and 126 matched controls. The longitudinal analysis involved 87 non-demented individuals (from population-based study) with two waves of plasma samples and three waves of functional magnetic resonance imaging during rest and memory encoding.
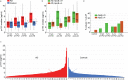
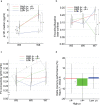
Results: Increased p-tau181 was observed for both ɛ4 carriers and non-carriers close to AD onset, but exclusively for ɛ4 carriers in the early preclinical groups (7- and 13-years pre-AD). In ɛ4 carriers, longitudinal p-tau181 increase was paralleled by elevated local hippocampal connectivity at rest and subsequent reduction of hippocampus encoding-related activity.
Conclusion: Our findings support an association of APOE ɛ4 and p-tau181 with preclinical AD and hippocampus functioning.
Keywords: APOE; Alzheimer’s disease; fMRI; hippocampus; longitudinal; magnetic resonance imaging; p-tau181; phosphorylated tau; population-based.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures
References
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261, 921–923. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Yamada K, Liddelow SA, Smith ST, Zhao L, Luo W, Tsai RM, Spina S, Grinberg LT, Rojas JC, Gallardo G, Wang K, Roh J, Robinson G, Finn MB, Jiang H, Sullivan PM, Baufeld C, Wood MW, Sutphen C, McCue L, Xiong C, Del-Aguila JL, Morris JC, Cruchaga C, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I, Fagan AM, Miller BL, Boxer AL, Seeley WW, Butovsky O, Barres BA, Paul SM, Holtzman DM (2017) ApoE4 markedly exacerbates tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature 549, 523–527. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Therriault J, Benedet AL, Pascoal TA, Mathotaarachchi S, Chamoun M, Savard M, Thomas E, Kang MS, Lussier F, Tissot C, Parsons M, Qureshi MNI, Vitali P, Massarweh G, Soucy JP, Rej S, Saha-Chaudhuri P, Gauthier S, Rosa-Neto P (2020) Association of Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 with medial temporal tau independent of amyloid-beta. JAMA Neurol 77, 470–479. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jack CR Jr. (2020) Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: A valid concept. Lancet Neurol 19, 31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

