Dauricine Attenuates Vascular Endothelial Inflammation Through Inhibiting NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 34925018
- PMCID: PMC8672219
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.758962
Dauricine Attenuates Vascular Endothelial Inflammation Through Inhibiting NF-κB Pathway
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Dauricine attenuates vascular endothelial inflammation through inhibiting NF-κB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 17;14:1236892. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1236892. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37663242 Free PMC article.
Abstract
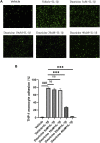
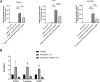
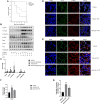
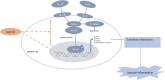
Endothelial cells are the fundamental components of blood vessels that regulate several physiological processes including immune responses, angiogenesis, and vascular tone. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to the development of various diseases such as acute lung injury, and endothelial inflammation is a vital part of endothelial dysfunction. Dauricine is an extract isolated from Menispermum dauricum DC, a traditional Chinese medical plant that can be used for pharyngitis. In this work, we found that IL-1β-induced overexpression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and E-selectin was inhibited by dauricine in primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Correspondingly, adhesion of human acute monocytic leukemia cell line (THP-1) to HUVECs was decreased by dauricine. Further studies showed that dauricine inhibited the activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway in HUVECs stimulated with IL-1β. In vivo, dauricine protected mice from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury. In lung tissues, the activation of NF-κB pathway and the expression of its downstream genes (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin) were decreased by dauricine, consistent with what was found in vitro. In summary, we concluded that dauricine could alleviate endothelial inflammation by suppressing NF-κB pathway, which might serve as an effective candidate for diseases related with endothelial inflammation.
Keywords: NF-κB pathway; acute lung injury; dauricine; endothelial dysfunction; inflammation.
Copyright © 2021 Hu, Chen, An, Wang, Liang and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chiang C. C., Cheng W. J., Lin C. Y., Lai K. H., Ju S. C., Lee C., et al. (2020). Kan-Lu-Hsiao-Tu-Tan, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula, Inhibits Human Neutrophil Activation and Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol 246, 112246. 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112246 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

