Integrated Network Pharmacology and Lipidomics to Reveal the Inhibitory Effect of Qingfei Oral Liquid on Excessive Autophagy in RSV-Induced Lung Inflammation
- PMID: 34925035
- PMCID: PMC8672039
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.777689
Integrated Network Pharmacology and Lipidomics to Reveal the Inhibitory Effect of Qingfei Oral Liquid on Excessive Autophagy in RSV-Induced Lung Inflammation
Abstract
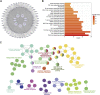
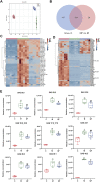
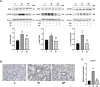
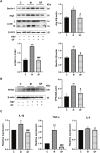
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can cause varying degrees of lung inflammation in children. Qingfei Oral Liquid (QF) is effective in treating childhood RSV-induced lung inflammation (RSV-LI) in clinics, but its pharmacological profiles and mechanisms remain unclear. Methods: This study combined network Pharmacology, lipidomics, pharmacodynamics, and pathway validation to evaluate the therapeutic mechanisms of QF. Using Cytoscape (v3.8.2) and enrichment analyses from the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Gene Ontology (GO), a global view of the putative compound-target-pathway network was created. The corresponding lipidomic profiles were then used to detect differently activated lipids, revealing the metabolic pathway, using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography linked to hybrid Quadrupole-Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap MS). Meanwhile, the in vivo efficiency of QF, the enrichment pathway, and the excessive autophagy inhibition mechanisms were validated in RSV-infected mice models. Results: The network pharmacology results demonstrated 117 active compounds acted directly upon 101 core targets of QF against RSV-LI. The most significantly enriched pathway was the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway (p < 0.05). In addition, untargeted lipidomics were performed, and it was revealed that higher lung levels of DAG 30:0, DAG 30:5, DAG 32:0, DAG 16:0_18:0, DAG 17:0_17:0, DAG 34:1, DAG 36:0, DAG 36:1 in the RSV-LI group were decreased after QF administration (FDR < 0.05, FC > 1.2). Lipin-1, a key enzyme in DAG synthesis, was increased in the RSV-LI mouse model. Animal experiments further validated that QF inhibited the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, with lower lung levels of phosphorylated PI3K, AKT and mTOR, as well as its related proteins of lipin-1 and VPS34 (p < 0.01). Finally, pharmacodynamic investigations indicated that QF reduced airway inflammation caused by excessive autophagy by decreasing lung levels of RSV F and G proteins, Beclin-1, Atg5, and LC3B II, IL-1 and TNF-α (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Lipidomic-based network pharmacology, along with experimental validation, may be effective approaches for illustrating the therapeutic mechanism of QF in the treatment of RSV-LI.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT/mTOR; excessive autophagy; lipidomics; lipin-1; network pharmacology; qingfei oral liquid; respiratory syncytial virus.
Copyright © 2021 Lin, An, Chen, Feng, Lu, Liu, Chu, Shan, Xie, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

