A Study on the Drug Concentration in Fellow Eyes After Unilateral Intravitreal Injection of Conbercept Into New Zealand Rabbit Eyes
- PMID: 34925038
- PMCID: PMC8672112
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.783057
A Study on the Drug Concentration in Fellow Eyes After Unilateral Intravitreal Injection of Conbercept Into New Zealand Rabbit Eyes
Abstract
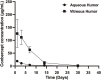
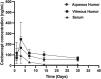
Intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have become increasingly popular in the treatment of ocular diseases. However, few studies have determined the efficiency of unilateral intravitreal anti-VEGF injection in the fellow eye. Herein, we performed a study to investigate the drug concentration in fellow eyes and venous serum after unilateral intravitreal injection of conbercept into rabbit eyes. This is an experimental animal study. Thirty male New Zealand rabbits (60 eyes) were used. One eye of each rabbit was intravitreally injected with 0.5 mg of conbercept. Both eyes from six rabbits were enucleated on days 1, 3, 7, 14, and 30. Conbercept concentrations were measured in the serum, aqueous humor, and vitreous humor. We found conbercept was detected in the fellow eyes and serum of rabbits. Conbercept concentrations in the vitreous humor of the fellow eyes increased from 74.11 ng/ml on day 1 to 246.69 ng/ml on day 3 and then declined to 69.11 ng/ml after 30 days. The concentration in the aqueous humor peaked on day 1 with a concentration of 244.82 ng/ml and declined to 40.13 ng/ml after 30 days. The maximum conbercept concentrations in the aqueous humor and vitreous humor of fellow eyes were similar, which were 0.2 and 1.3% of those of the injected eye, respectively. A peak concentration of 102.49 ng/ml was achieved in the venous serum 1 day after intravitreal injection of conbercept, which was 0.08 and 0.5% of those of the maximum conbercept concentrations in the vitreous humor and aqueous humor of the injected eye, respectively, and 41.5 and 41.8% of the maximum conbercept concentrations in the vitreous humor and aqueous humor of the non-injected eye, respectively. In conclusion, after intravitreal injection of 0.5 mg of conbercept into rabbit eyes, very small amounts of conbercept were detected in the fellow non-injected eyes and venous serum.
Keywords: aqueous humor; conbercept; drug concentration; non-injected eyes; serum; vitreous.
Copyright © 2021 Di, Xu, Ye and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin).Ophthalmology. 2007 May;114(5):855-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.01.017. Ophthalmology. 2007. PMID: 17467524
-
Pharmacokinetics of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin®) in rabbits.Clin Ophthalmol. 2011;5:697-704. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S19555. Epub 2011 May 24. Clin Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21629577 Free PMC article.
-
Observation of total VEGF level in hyperglycemic mouse eyes after intravitreal injection of the novel anti-VEGF drug conbercept.Mol Vis. 2015 Feb 20;21:185-93. eCollection 2015. Mol Vis. 2015. PMID: 25737631 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intravitreal conbercept injection on VEGF-A and -B levels in the aqueous and vitreous humor of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Apr;21(4):332. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9763. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33732305 Free PMC article.
-
Anaphylatoxin concentration in aqueous and vitreous humor in the eyes with vitreoretinal interface abnormalities.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Jun;195:108025. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108025. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32224205 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Anti-Angiogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Nanoformulation for Effective Treatment of Ocular Vascular Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jan 24;18:437-453. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S387428. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36718193 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular pharmacokinetics of intravitreal conbercept in a rabbit model following retinal scatter laser photocoagulation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 7;16:1534048. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1534048. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40260388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avery R. L., Castellarin A. A., Steinle N. C., Dhoot D. S., Joseph Pieramici D., See R., et al. (2014). Systemic Pharmacokinetics Following Intravitreal Injections of Ranibizumab, Bevacizumab or Aflibercept in Patients with Neovascular AMD. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 98, 1636–1641. 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2014-305252 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

