A Case of Hypopharyngeal Cancer Associated With Fanconi Anemia: A Helical Tomotherapy Experience
- PMID: 34925988
- PMCID: PMC8654145
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.19386
A Case of Hypopharyngeal Cancer Associated With Fanconi Anemia: A Helical Tomotherapy Experience
Abstract
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a disease that could be accompanied by multiple abnormalities, such as growth retardation, bone marrow abnormalities, and cancer susceptibility. Among the FA patients, head and neck squamous cell cancer (HNSCC) is the most observed solid cancer. The life expectancy of patients with FA has increased with recent medical advances. Furthermore, HNSCC is diagnosed in 3% of FA patients, and half of these patients die because of their HNSCC. The median age of HNSCC patients with FA is 31, and according to the literature HNSCC incidence of FA, patients is more than 700-fold of the normal population. Here, we reported the treatment details and challenges we faced during hypopharyngeal cancer treatment in a FA patient.
Keywords: aplastic anemia; cetuximab; concomitant chemo-radiation therapy; fanconi anemia; head and neck squamous cell cancer; helical imrt; radiation therapy; tomotherapy.
Copyright © 2021, Kavak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
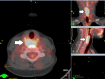
Figures

References
-
- Bhandari J, Thada PK, Puckett Y. StatPearls Publishing. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Fanconi Anemia. - PubMed
-
- High incidence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in patients with Fanconi anemia. Kutler DI, Auerbach AD, Satagopan J, et al. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;129:106–112. - PubMed
-
- A 20-year perspective on the International Fanconi Anemia Registry (IFAR) Kutler DI, Singh B, Satagopan J, et al. Blood. 2003;101:1249–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
