Evaluation of LMR, NLR and PLR as predictors of malignancy in indeterminate thyroid nodules
- PMID: 34928264
- PMCID: PMC8686799
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-N1515
Evaluation of LMR, NLR and PLR as predictors of malignancy in indeterminate thyroid nodules
Abstract
Objective: Thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology represent 20% of all thyroid nodules. Inflammation plays an important role in cancer. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) are independent prognostic scores in numerous cancers, although no study has documented their role in cytology indeterminate nodules. The aim of this study is to evaluate the role of LMR, NLR and PLR values as predictors of malignancy in patients with cytology indeterminate nodules.
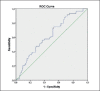
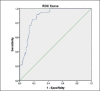
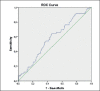
Methods: This retrospective study analysed data from 298 patients with indeterminate thyroid nodule. Anatomopathological and haematological data were analysed, dividing the population into two groups. LMR, NLR and PLR values were determined using ROC curve and data were analysed using independent samples t-test, test of proportions, Fisher's exact test and univariate and multivariate logistic regression.
Results: We found that a baseline LMR value ≥ 4.09 was indicative of benignity of indeterminate nodule. The probability of malignancy in patients with LMR < 4.09 was 26 times higher than patients with a LMR value ≥ 4.09.
Conclusions: This study showed that only LMR has shown a concrete probability to find a thyroid cancer in patients with indeterminate nodules. Further studies are necessary to implement tailored treatment.
Valutazione di LMR, NLR e PLR come predittori di malignità in noduli tiroidei indeterminati.
Obiettivo: I noduli tiroidei a citologia indeterminata rappresentano il 20% di tutti i noduli tiroidei. L’infiammazione gioca un ruolo importante nel cancro. LMR, NLR e PLR sono fattori prognostici indipendenti in numerosi tumori; tuttavia, nessuno studio ha mostrato il loro ruolo nei noduli a citologia indeterminata. Questo studio si propone di valutare il ruolo di LMR, NLR e PLR come predittori di malignità in pazienti con noduli a citologia indeterminata.
Metodi: Abbiamo analizzato retrospettivamente i dati di 298 pazienti con nodulo tiroideo indeterminato. Abbiamo analizzato i dati anatomopatologici ed ematologici, dividendo la popolazione in due gruppi. I valori cut-off di LMR, NLR e PLR sono stati determinati con la curva ROC e i dati sono stati esaminati utilizzando il t-test per campioni indipendenti, il test delle proporzioni, il Fisher exact test e la regressione univariata e multivariata.
Risultati: Un valore LMR basale ≥ 4,09 è indicativo di benignità. La probabilità di neoplasia nei pazienti con LMR < 4,09 è 26 volte superiore rispetto ai pazienti con valore LMR ≥ 4,09.
Conclusioni: Questo studio ha dimostrato che solo un valore di LMR < 4,09 ha una probabilità concreta che un nodulo a citologia indeterminata possa essere un cancro.
Keywords: indeterminate thyroid nodule; lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; thyroid cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria e Chirurgia Cervico-Facciale, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, et al. American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2015;26:1-133. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2015.0020 10.1089/thy.2015.0020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kitahara CM, Sosa JA. The changing incidence of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2016;12:646-653. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.110 10.1038/nrendo.2016.110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cabanillas ME, McFadden DG, Durante C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet 2016;388:2783-2795. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30172-6 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30172-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gambardella C, Patrone R, Di Capua F, et al. The role of prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in elderly patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: a multicentric study. BMC Surg 2019;18(Suppl 1):110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0433-0 10.1186/s12893-018-0433-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nardi F, Basolo F, Crescenzi A, et al. Italian Consensus for the classification and reporting of thyroid cytology. J Endocrinol Invest 2014;37:593-599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0062-0 10.1007/s40618-014-0062-0 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

