Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response 4 Weeks After Homologous vs Heterologous Third Vaccine Dose in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 34928302
- PMCID: PMC8689434
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.7372
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response 4 Weeks After Homologous vs Heterologous Third Vaccine Dose in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Fewer than 50% of kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) develop antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein after 2 doses of an mRNA vaccine. Preliminary data suggest that a heterologous vaccination, combining mRNA and viral vector vaccines, may increase immunogenicity.
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of a third dose of an mRNA vs a vector vaccine in KTRs who did not have antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein after 2 doses of an mRNA vaccine.
Design, setting, and participants: This was a single center, single-blinded, 1:1 randomized clinical trial of a third dose of vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, conducted from June 15 to August 16, 2021, in 201 KTRs who had not developed SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibodies after 2 doses of an mRNA vaccine. Data analyses were performed from August 17 to August 31, 2021.
Interventions: mRNA (BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273) or vector (Ad26COVS1) as a third dose of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary study end point was seroconversion after 4 weeks (29-42 days) following the third vaccine dose. Secondary end points included neutralizing antibodies and T-cell response assessed by interferon-γ release assays (IGRA). In addition, the association of patient characteristics and vaccine response was assessed using logistic regression, and the reactogenicity of the vaccines was compared.
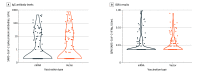
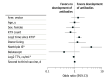
Results: Among the study population of 197 kidney transplant recipients (mean [SD] age, 61.2 [12.4] years; 82 [42%] women), 39% developed SARS-CoV-2 antibodies after the third vaccine. There was no statistically significant difference between groups, with an antibody response rate of 35% and 42% for the mRNA and vector vaccines, respectively. Only 22% of seroconverted patients had neutralizing antibodies. Similarly, T-cell response assessed by IGRA was low with only 17 patients showing a positive response after the third vaccination. Receiving nontriple immunosuppression (odds ratio [OR], 3.59; 95% CI, 1.33-10.75), longer time after kidney transplant (OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.15-1.83, per doubling of years), and torque teno virus plasma levels (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.88-0.96, per doubling of levels) were associated with vaccine response. The third dose of an mRNA vaccine was associated with a higher frequency of local pain at the injection site compared with the vector vaccine, while systemic symptoms were comparable between groups.
Conclusions and relevance: This randomized clinical trial found that 39% of KTRs without an immune response against SARS-CoV-2 after 2 doses of an mRNA vaccine developed antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein 4 weeks after a third dose of an mRNA or a vector vaccine. The heterologous vaccination strategy with a vector-based vaccine was well tolerated and safe but not significantly better than the homologous mRNA-based strategy.
Trial registration: EudraCT Identifier: 2021-002927-39.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

