Rates in Bronchiolitis Hospitalization, Intensive Care Unit Use, Mortality, and Costs From 2004 to 2018
- PMID: 34928313
- PMCID: PMC8689435
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.5177
Rates in Bronchiolitis Hospitalization, Intensive Care Unit Use, Mortality, and Costs From 2004 to 2018
Abstract
Importance: Over the last 2 decades, bronchiolitis guidelines and improvement efforts focused on supportive care and reducing unnecessary tests, treatments, and hospitalization. There have been limited population-based studies examining hospitalization outcomes over time.
Objective: To describe rates and trends in bronchiolitis hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) use, mortality, and costs.
Design, setting, and participants: This cohort study used population-based health administrative data from April 1, 2004, to March 31, 2018, to identify bronchiolitis encounters using hospital discharge diagnosis codes in Ontario, Canada. Children younger than 2 years with and without bronchiolitis hospitalization were included. Data were analyzed from January 2020 to July 2021.
Main outcomes and measures: Bronchiolitis hospitalization per 1000 person-years, ICU use per 1000 hospitalizations, mortality per 100 000 person-years, and costs per 1000 person-years adjusted to 2018 Canadian dollars and reported in 2018 US dollars.
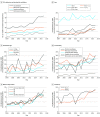
Results: Among 2 336 446 included children, 1 199 173 (51.3%) were male. During the study period, 43 993 children (1.9%) younger than 2 years had 48 058 bronchiolitis hospitalizations at 141 hospitals. Bronchiolitis accounted for 48 058 of 360 920 all-cause hospitalizations (13.3%) and 215 654 of 2 566 348 all-cause hospital days (8.4%) in children younger than 2 years. Bronchiolitis hospitalization was stable over time, at 14.0 (95% CI, 13.6-14.4) hospitalizations per 1000 person-years in 2004-2005 and 12.7 (95% CI, 12.2-13.1) hospitalizations per 1000 person-years in 2017-2018 (annual percent change [APC], 0%; 95% CI, -1.6 to 1.6; P = .97). ICU admission increased significantly from 38.1 (95% CI, 32.2-44.8) per 1000 hospitalizations in 2004-2005 to 87.8 (95% CI, 78.3-98.0) per 1000 hospitalizations in 2017-2018 (APC, 7.2%; 95% CI, 5.4-8.9; P < .001). Over the study period, bronchiolitis mortality was 2.8 (95% CI, 2.3-3.4) per 100 000 person-years and remained stable (APC, 1.1%; 95% CI, -8.4 to 11.7; P = .85). Hospitalization costs per 1000 person-years increased from $49 640 (95% CI, $49 617-$49 663) in 2004-2005 to $58 632 (95% CI, $58 608-$58 657) in 2017-2018 (APC, 3.0%; 95% CI, 1.3-4.8; P = .002).
Conclusions and relevance: From 2004 to 2018, bronchiolitis hospitalization and mortality rates remained stable; however, ICU use and costs increased substantially. This represents a major increase in high-intensity hospital care and costs for one of the most common and cumulatively expensive conditions in pediatric hospital care.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Why Are So Many Children With Bronchiolitis Going to the Intensive Care Unit?JAMA Pediatr. 2022 Mar 1;176(3):231-233. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.5186. JAMA Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 34928316 No abstract available.
References
-
- Friedman JN, Rieder MJ, Walton JM; Canadian Paediatric Society, Acute Care Committee, Drug Therapy and Hazardous Substances Committee . Bronchiolitis: recommendations for diagnosis, monitoring and management of children one to 24 months of age. Paediatr Child Health. 2014;19(9):485-498. doi: 10.1093/pch/19.9.485 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

