Working with the natural complexity: Selection and characterization of black cohosh root extract for use in toxicology testing
- PMID: 34929352
- PMCID: PMC9063431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112769
Working with the natural complexity: Selection and characterization of black cohosh root extract for use in toxicology testing
Abstract
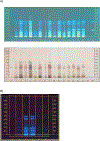
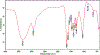
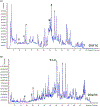
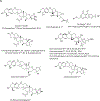
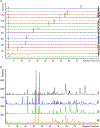
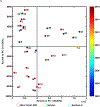
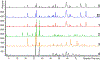
Black cohosh (Actaea racemosa L.) is a botanical supplement marketed to women of all ages. Due to paucity of data to assess the safe use, the National Toxicology Program (NTP) is evaluating the toxicity of black cohosh. The use of an authentic, quality material is imperative to generate robust data. Because botanical materials are complex mixtures with variable composition, the selection of a material is challenging. We describe selection and phytochemical characterization of an unformulated black cohosh root extract (i.e., an extract that serves as source material for a formulated product) to be used in the NTP assessments. A material was selected using a combination of non-targeted and targeted chemical analyses, including confirmation of authenticity, absence of contaminants and adulterants, and similarity to a popular black cohosh product used by consumers. Thirty-nine constituents covering three major classes, triterpene glycosides, phenolic acids, and alkaloids were identified. Among constituents quantified, triterpene glycosides made up approximately 4.7% (w/w) with total constituents quantified making up 5.8% (w/w) of the extract. Non-targeted chemical analysis followed by chemometric analysis of various materials sold as black cohosh, and reference materials for black cohosh and other Actaea species further confirmed the suitability of the selected extract for use.
Keywords: Black cohosh; Botanical dietary supplements; Constituents; Phytochemical composition.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no competing interests
Figures







References
-
- AHP, 2002. American Herbal Pharmacopeia. Black Cohosh Rhizom, Actaea racemosa L. syn. Cimicifuga racemosa (L.) Nutt.Standards of Analysis, Quality Control, and Therapeutics, in: Upton R (Ed.), AmericanHerbal Pharmacopoeia and Therapeutic Compendium, Santa Cruz, CA, USA.
-
- AHPA, 2009. American Herbal Products Association. Heavy Metals: Analysis and Limits in Herbal Dietary Supplements.
-
- Baker DA, Stevenson DW, Little DP, 2012. DNA barcode identification of black cohosh herbal dietary supplements. J AOAC Int 95, 1023–1034. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

