Comorbidities and mortality in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 34929892
- PMCID: PMC8677356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2021.10.085
Comorbidities and mortality in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background: The high mortality rate in Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) patients is associated with their comorbid conditions. Therefore, it is important to identify risk factors associated with poor outcomes among COVID-19 patients. The aims of this study were to find out the comorbidities in case of death due to COVID-19.
Methods: The design of this study was a retrospective descriptive method with a confirmed COVID-19 patient on hospitalized at Dr. Wahidin Sudirohusodo Hospital from March to September 2020. Ethics Council recommendation number: 357/UN4.6.4.5.31/PP36/2020.
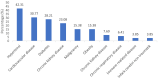
Results: A total of 454 patients were included of this study. 78 (17.18%) patients death due to COVID-19, consisting of 52 (66.67%) male and 26 (33.33%) female. Range of ages between 18 and 85 years. The highest mortality rate occurred in the age group ≥60 years (35; 51.47%), followed by the age group of 45-59 years (33; 48.53%), and the age group of <45 years (10; 12%). The prevalent comorbidity was hypertension (42.31%), cardiovascular disease (30.77%), diabetes (28.21%), chronic kidney disease (23.08%), malignancy (15.38%), obesity (15.38%), chronic liver disease (7.69%), chronic respiratory disease (6.41%), immune related disease (3.85%), and non-traumatic cerebral infarction (3.85%). 41 (52.56%) patients reported having two or more comorbidities, and 37 (47.44%) only has one comorbidity. Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) ≥3.13 was seen in the majority of patients (68; 87.18%). The mean value of NLR was 20.94.
Conclusions: Hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes were the most common comorbidity in patients death due to COVID-19. More than half of the patients had two or more comorbidities.
Keywords: COVID-19; Comorbidities; Mortality.
Copyright © 2021 SESPAS. Publicado por Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease 2019 Situation Report 51-11th March 2020. WHO Bull. 2020; 2019: 2633.
-
- WHO Indonesia. Coronavirus Disease Situation Report World Health Organization. World Heal Organ. 2020; 19:1–17.
-
- Hua W., Xiaofeng L., Zhenqiang B., et al. Consideration on the strategies during epidemic stage changing from emergency response to continuous prevention and control. Chinese J Endem. 2020;41:297–300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials