Real-world impact of fremanezumab on migraine symptoms and resource utilization in the United States
- PMID: 34930112
- PMCID: PMC8903530
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-021-01358-9
Real-world impact of fremanezumab on migraine symptoms and resource utilization in the United States
Abstract
Background: Fremanezumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibody (IgG2Δa) that selectively targets calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), is approved for migraine prevention in adults. Real-world data on the effectiveness of fremanezumab are limited. This retrospective, observational cohort study assessed patient-reported migraine symptoms, health care resource utilization (HCRU), and direct medical costs before and after fremanezumab treatment initiation.
Methods: Data were extracted from September 2018 through June 2020 from the Midwest component of EMRClaims+®, an integrated health services database containing > 20 million medical records from national commercial insurance claims, Medicare claims, and regional electronic medical records. Patients included in the cohort analysis were aged ≥ 18 years and were administered fremanezumab, with enrollment or treatment history for ≥ 6 months prior (pre-index) to initiating fremanezumab (index date) and ≥ 1 month after the index date (post-index), and without pregnancy or pregnancy-related encounters during the study period. Patient-reported headache frequency, migraine pain intensity (MPI), composite migraine symptoms, and HCRU were assessed pre-index and ≥ 1 month after fremanezumab initiation. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests were used to compare means of migraine symptoms and outcomes and HCRU before and after fremanezumab initiation.
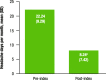
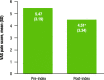
Results: Overall, 172 patients were eligible for analysis. Of patients who self-reported (n = 129), 83.7% reported improvement in headache frequency or symptoms after fremanezumab treatment. Specifically, headache frequency decreased by 63% after fremanezumab initiation: mean (standard deviation) headache frequency was 22.24 (9.29) days per month pre-index versus 8.24 (7.42) days per month post-index (P < 0.0001). Mean MPI also decreased by 18% after fremanezumab initiation: MPI was 5.47 (3.19) pre-index versus 4.51 (3.34) post-index (P = 0.014). Mean emergency room (ER) visits per month decreased from 0.72 to 0.54 (P = 0.003), and mean outpatient visits per month decreased from 1.04 to 0.81 (P < 0.001). Mean hospitalizations per month decreased, but the results did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.095). Hospitalization and ER costs decreased, while outpatient costs increased, from pre-index to post-index, but differences were not statistically significant (P ≥ 0.232).
Conclusions: Significant reductions in headache frequency, MPI, and HCRU were observed after fremanezumab initiation in patients with migraine in a US real-world setting.
Keywords: Fremanezumab; Headache frequency; Health care resource utilization; Migraine; Migraine pain intensity; Real-world efficacy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
PM has received research support from Amgen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Alder BioPharmaceuticals; and serves as a consultant for Amgen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Alder BioPharmaceuticals. LL is an employee of Henry Ford Health System, with research funding from eMAX Health Systems. JC and ZD are employees of eMAX Health Systems. LJK, ST, and MD are employees of Teva Pharmaceuticals. JMC and KT are former employees of Teva Pharmaceuticals. AM has nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
US Real-World Effectiveness, Tolerability, and Healthcare Resource Utilization After Addition of Fremanezumab for Preventive Treatment in Patients Using Gepants for Acute Treatment of Migraine: Results From a Retrospective Chart Review.Adv Ther. 2025 Feb;42(2):1207-1221. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-03063-w. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 39775579 Free PMC article.
-
Health care resource utilization and direct costs incurred over 12 months by patients with migraine initiating self-injectable calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies: A US real-world study.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2025 Apr;31(4):351-365. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2025.31.4.351. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40152794 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world Impact of Fremanezumab on Migraine-Related Health Care Resource Utilization in Patients with Comorbidities, Acute Medication Overuse, and/or Unsatisfactory Prior Migraine Preventive Response.Pain Ther. 2024 Jun;13(3):511-532. doi: 10.1007/s40122-024-00583-9. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Pain Ther. 2024. PMID: 38472655 Free PMC article.
-
Fremanezumab: a disease-specific option for the preventive treatment of migraine, including difficult-to-treat migraine.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020 Sep 8;4(2):179-190. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20200018. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32832978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fremanezumab for the Treatment of Migraine Complicated by Medication Overuse: A Systematic Review.Clin Drug Investig. 2025 May;45(5):247-254. doi: 10.1007/s40261-025-01433-y. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Clin Drug Investig. 2025. PMID: 40121372
Cited by
-
Real-world effectiveness of Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies compared to OnabotulinumtoxinA (RAMO) in chronic migraine: a retrospective, observational, multicenter, cohort study.J Headache Pain. 2024 Feb 2;25(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01721-6. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 38308209 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing the Impact of Headache and Allodynia Score in Chronic Migraine: An Exploratory Analysis from the Real-World Effectiveness of Anti-CGRP Monoclonal Antibodies Compared to Onabotulinum Toxin A (RAMO) Study.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Apr 7;16(4):178. doi: 10.3390/toxins16040178. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668603 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibodies in the Prevention of Migraine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Cohort Studies.Clin Drug Investig. 2023 Sep;43(9):669-680. doi: 10.1007/s40261-023-01301-7. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Clin Drug Investig. 2023. PMID: 37665501
-
US Real-World Effectiveness, Tolerability, and Healthcare Resource Utilization After Addition of Fremanezumab for Preventive Treatment in Patients Using Gepants for Acute Treatment of Migraine: Results From a Retrospective Chart Review.Adv Ther. 2025 Feb;42(2):1207-1221. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-03063-w. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 39775579 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal Antibodies against Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide for Migraine Prophylaxis: A Systematic Review of Real-World Data.Cells. 2022 Dec 29;12(1):143. doi: 10.3390/cells12010143. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buse DC, Loder EW, Gorman JA, Stewart WF, Reed ML, Fanning KM, et al. Sex differences in the prevalence, symptoms, and associated features of migraine, probable migraine and other severe headache: results of the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) study. Headache. 2013;53:1278–1299. doi: 10.1111/head.12150. - DOI - PubMed
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials