The use of oxygen reserve index in one-lung ventilation and its impact on peripheral oxygen saturation, perfusion index and, pleth variability index
- PMID: 34930139
- PMCID: PMC8685494
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-021-01539-8
The use of oxygen reserve index in one-lung ventilation and its impact on peripheral oxygen saturation, perfusion index and, pleth variability index
Abstract
Background: Our goal is to investigate the use of the oxygen reserve index (ORi) to detect hypoxemia and its relation with parameters such as; peripheral oxygen saturation, perfusion index (PI), and pleth variability index (PVI) during one-lung ventilation (OLV).
Methods: Fifty patients undergoing general anesthesia and OLV for elective thoracic surgeries were enrolled in an observational cohort study in a tertiary care teaching hospital. All patients required OLV after a left-sided double-lumen tube insertion during intubation. The definition of hypoxemia during OLV is a peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) value of less than 95%, while the inspired oxygen fraction (FiO2) is higher than 50% on a pulse oximetry device. ORi, pulse oximetry, PI, and PVI values were measured continuously. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, likelihood ratios, and accuracy were calculated for ORi values equal to zero in different time points during surgery to predict hypoxemia. At Clinicaltrials.gov registry, the Registration ID is NCT05050552.
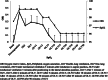
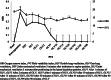
Results: Hypoxemia was observed in 19 patients (38%). The accuracy for predicting hypoxemia during anesthesia induction at ORi value equals zero at 5 min after intubation in the supine position (DS5) showed a sensitivity of 92.3% (95% CI 84.9-99.6), specificity of 81.1% (95% CI 70.2-91.9), and an accuracy of 84.0% (95% CI 73.8-94.2). For predicting hypoxemia, ORi equals zero show good sensitivity, specificity, and statistical accuracy values for time points of DS5 until OLV30 where the sensitivity of 43.8%, specificity of 64%, and an accuracy of 56.1% were recorded. ORi and SpO2 correlation was found at DS5, 5 min after lateral position with two-lung ventilation (DL5) and at 10 min after OLV (OLV10) (p = 0.044, p = 0.039, p = 0.011, respectively). Time-dependent correlations also showed that; at a time point of DS5, ORi has a significant negative correlation with PI whereas, no correlations with PVI were noted.
Conclusions: During the use of OLV for thoracic surgeries, from 5 min after intubation (DS5) up to 30 min after the start of OLV, ORi provides valuable information in predicting hypoxemia defined as SpO2 less than 95% on pulse oximeter at FiO2 higher than 50%.
Keywords: Hypoxemia; One lung ventilation; Oxygen reserve index; Perfusion index; Pleth variability index.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oxygen Reserve Index Predicts Hypoxemia During One-Lung Ventilation: An Observational Diagnostic Study.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020 Feb;34(2):417-422. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2019.06.035. Epub 2019 Jun 28. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020. PMID: 31362907
-
Oxygen reserve index guided oxygen titration in one lung ventilation with low fresh gas flow.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Oct 21;51(5):2413-2419. doi: 10.3906/sag-2009-149. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34051711
-
Predicting intraoperative hypoxemia in lung resection surgery: assessing the utility of oxygen reserve index measurements during one-lung ventilation before pleural opening.J Clin Monit Comput. 2025 Jun;39(3):631-639. doi: 10.1007/s10877-025-01278-y. Epub 2025 Feb 26. J Clin Monit Comput. 2025. PMID: 40011394
-
ORi™: a new indicator of oxygenation.J Anesth. 2021 Oct;35(5):734-740. doi: 10.1007/s00540-021-02938-4. Epub 2021 Apr 26. J Anesth. 2021. PMID: 33900455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxemia during one-lung ventilation: prediction, prevention, and treatment.Anesthesiology. 2009 Jun;110(6):1402-11. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31819fb15d. Anesthesiology. 2009. PMID: 19417615 Review.
Cited by
-
Perioperative monitoring of the oxygen reserve: where do we stand?J Clin Monit Comput. 2023 Dec;37(6):1431-1433. doi: 10.1007/s10877-023-01085-3. Epub 2023 Oct 21. J Clin Monit Comput. 2023. PMID: 37863861
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficiency and Safety of Double-Lumen Tube and Bronchial Blocker for One-Lung Ventilation.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 27;12(5):1877. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051877. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Oxygen Reserve index and arterial partial pressure of oxygen during one-lung ventilation: a retrospective cohort study.J Anesth. 2023 Dec;37(6):938-944. doi: 10.1007/s00540-023-03259-4. Epub 2023 Oct 3. J Anesth. 2023. PMID: 37787833
-
Tailored single-lung ventilation approaches and postoperative pulmonary outcomes in thoracic surgery.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Jul 31;17(7):5371-5387. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2025-314. Epub 2025 Jul 28. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40809239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yoon S, Kim BR, Min SH, Lee J, Bahk JH, Seo JH. Repeated intermittent hypoxic stimuli to operative lung reduce hypoxemia during subsequent one-lung ventilation for thoracoscopic surgery: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(4):e0249880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249880. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

