Long-term oncologic safety of immediate reconstructive surgery in patients with invasive breast cancer: a retrospective matched-cohort study
- PMID: 34930333
- PMCID: PMC8686330
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-021-02450-9
Long-term oncologic safety of immediate reconstructive surgery in patients with invasive breast cancer: a retrospective matched-cohort study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Long-term oncologic safety of immediate reconstructive surgery in patients with invasive breast cancer: a retrospective matched-cohort study.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Feb 28;20(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02523-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35227268 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
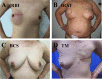
Objective: Immediate reconstruction (IR) is a safe and effective surgical treatment for patients with breast cancer. We aimed to assess the prognosis, aesthetic outcomes, and patient satisfaction of IR compared with breast conservation surgery (BCS) and total mastectomy (TM).
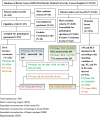
Methods: This retrospective matched-cohort study was conducted between May 2005 and December 2014. We established two cohorts according to the tumor (T) size of breast cancer. In the T≤3cm group, cases (IR) and controls (BCS or TM) were matched for age, pathological tumor size, and pathologic nodal status in a 1:1:1 ratio. In the T>3cm group, cases (IR) and controls (TM) were matched with the same factors and ratio. The primary outcome was the 5-year disease-free survival (DFS). The secondary outcome was patient satisfaction and quality of life.
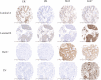
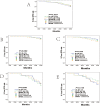
Results: A total of 12,678 breast cancer patients were assessed for eligibility, of which 587 were included (T≤3 cm group: 155 IR vs 155 BCS vs 155 TM; T>3cm group: 61 IR vs 61 TM). In the T≤3 cm cohort, patients who underwent IR had no difference compared with those who underwent BCS or TM regarding the 5-year DFS (P=0.539); however, an improved aesthetic satisfaction, psychosocial, and sexual well-being were achieved in the IR group (P<0.001). In the T>3 cm cohort, the IR group had a worse median 5-year DFS (P=0.044), especially for Her2+ or triple-negative breast carcinoma (TNBC) subtypes compared with the TM group.
Conclusions: IR improves aesthetic satisfaction, psychosocial, and sexual well-being for breast cancer patients with T≤3 cm. For patients with T > 3 cm invasive breast cancer, TM is superior to IR as it predicts a better 5-year DFS.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Breast conservation surgery; Breast reconstruction; Modified radical mastectomy; Patient satisfaction; Prognosis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

