Ribociclib-associated organising pneumonia
- PMID: 34930762
- PMCID: PMC8689130
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-245187
Ribociclib-associated organising pneumonia
Abstract
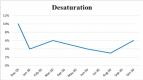
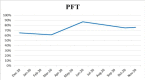
A 63-year-old woman with grade 2 infiltrating left breast carcinoma who was started on ribociclib complained of exertional dyspnoea along with dry cough. There were bilateral interscapular crackles and chest X-ray evidence of bilateral mid and lower zone non-homogeneous opacity. The patient's pulmonary function test (PFT) showed moderate restrictions and desaturation. CT was suggestive of organising pneumonia and drug administration was stopped. The patient was treated with steroids in tapering doses, which led to improvements. The drug was restarted with the probability of other aetiologies for interstetial lung disease (ILD). It was also considered the superior efficacy of ribociclib in managing breast cancer. But due to evidence indicating the reappearance of organising pneumonia following drug administration, it was again stopped, and steroid use was restarted for treatment. The patient showed improvements in subsequent follow-ups.
Keywords: breast cancer; interstitial lung disease; pneumonia (respiratory medicine).
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures







References
-
- D’souza M, Rajiah P, Irion K. Radiological imaging of drug-induced PulmonaryLesions. J Clin Radiol Case Rep 2018;2:2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
