A counter-enzyme complex regulates glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 34931064
- PMCID: PMC8810680
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-021-00919-y
A counter-enzyme complex regulates glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
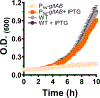
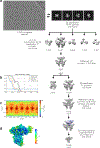
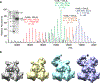
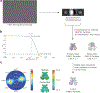
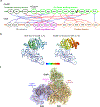
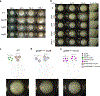
Multi-enzyme assemblies composed of metabolic enzymes catalyzing sequential reactions are being increasingly studied. Here, we report the discovery of a 1.6 megadalton multi-enzyme complex from Bacillus subtilis composed of two enzymes catalyzing opposite ('counter-enzymes') rather than sequential reactions: glutamate synthase (GltAB) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GudB), which make and break glutamate, respectively. In vivo and in vitro studies show that the primary role of complex formation is to inhibit the activity of GudB. Using cryo-electron microscopy, we elucidated the structure of the complex and the molecular basis of inhibition of GudB by GltAB. The complex exhibits unusual oscillatory progress curves and is necessary for both planktonic growth, in glutamate-limiting conditions, and for biofilm growth, in glutamate-rich media. The regulation of a key metabolic enzyme by complexing with its counter enzyme may thus enable cell growth under fluctuating glutamate concentrations.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests:
The authors declare no conflict of interests
Figures


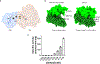

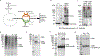
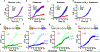
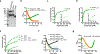

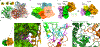
Comment in
-
A complex struggle for direction.Nat Chem Biol. 2022 Feb;18(2):119-120. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00937-w. Nat Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 34931063 No abstract available.
References
-
- Curi R et al. Regulatory principles in metabolism -Then and now. Biochemical Journal vol. 473 1845–1857 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Srere PA The metabolon. Trends in Biochemical Sciences vol. 10 109–110 (1985).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

