Anthrax toxins regulate pain signaling and can deliver molecular cargoes into ANTXR2+ DRG sensory neurons
- PMID: 34931070
- PMCID: PMC9388775
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-021-00973-8
Anthrax toxins regulate pain signaling and can deliver molecular cargoes into ANTXR2+ DRG sensory neurons
Abstract
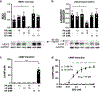
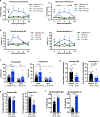
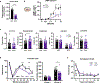
Bacterial products can act on neurons to alter signaling and function. In the present study, we found that dorsal root ganglion (DRG) sensory neurons are enriched for ANTXR2, the high-affinity receptor for anthrax toxins. Anthrax toxins are composed of protective antigen (PA), which binds to ANTXR2, and the protein cargoes edema factor (EF) and lethal factor (LF). Intrathecal administration of edema toxin (ET (PA + EF)) targeted DRG neurons and induced analgesia in mice. ET inhibited mechanical and thermal sensation, and pain caused by formalin, carrageenan or nerve injury. Analgesia depended on ANTXR2 expressed by Nav1.8+ or Advillin+ neurons. ET modulated protein kinase A signaling in mouse sensory and human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived sensory neurons, and attenuated spinal cord neurotransmission. We further engineered anthrax toxins to introduce exogenous protein cargoes, including botulinum toxin, into DRG neurons to silence pain. Our study highlights interactions between a bacterial toxin and nociceptors, which may lead to the development of new pain therapeutics.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
S.M.L., S.P., S.M., J.M., V.T. and K.A.F. are employees of Ipsen. I.M.C. has received sponsored research support from Ipsen, GSK and Allergan Pharmaceuticals, and is a member of scientific advisory boards for GSK and Kintai Pharmaceuticals. This work is related to patent applications PCT/US16/49099 and PCT/US16/49106, “Compositions and methods for treatment of pain,” of which R.J.C., I.M.C., B.L.P., K.A.F., S.P. and S.M.L. are co-inventors. O.B. is a co-founder and shareholder of LIFE & BRAIN GmbH. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

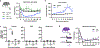





Comment in
-
Harnessing bacterial toxins to treat pain.Nat Neurosci. 2022 Feb;25(2):132-134. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00981-8. Nat Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34931071 No abstract available.
References
REFERENCES FOR METHODS
-
- Wu C, Macleod I & Su AI BioGPS and MyGene.info: organizing online, gene-centric information. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D561–565 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lein ES et al. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 445, 168–176 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Abrahamsen B et al. The Cell and Molecular Basis of Mechanical, Cold, and Inflammatory Pain. Science 321, 702–705 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

